Delving into the distance between Earth and Mars offers a captivating journey into the world of astronomy and space exploration. This topic not only highlights the vastness of our solar system but also underscores the challenges that scientists and engineers face in their quest to explore the Red Planet. Whether you're a student, a scientist, or just someone with a curiosity about space, this guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the subject.
The distance between Earth and Mars is not static but fluctuates considerably due to their elliptical orbits around the Sun. This variability makes understanding the factors influencing this distance essential for planning space missions, designing spacecraft, and ensuring successful exploration. This article will take you on a detailed exploration of this cosmic phenomenon, covering everything from the basics to advanced concepts.
From the early observations of ancient astronomers to the cutting-edge missions of today, humanity's fascination with Mars has only deepened over time. This article aims to provide a thorough examination of the distance from Earth to Mars, exploring its implications for both current and future space endeavors. Join us on this fascinating journey through the cosmos!
- Millbutn Deli
- Amc Independence Commons 20 Theater
- How Old Jack Black
- La Catrina Mexican Grill
- Country Hills Ford
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Earth-Mars Distance
- Understanding the Orbits of Earth and Mars
- Variations in the Distance from Earth to Mars
- The Closest Approach of Mars to Earth
- The Farthest Distance between Earth and Mars
- How Long Does It Take to Travel from Earth to Mars?
- Space Missions to Mars
- Technological Challenges in Mars Exploration
- Future Plans for Mars Exploration
- Conclusion
Exploring the Dynamics of Earth-Mars Distance
Understanding the distance between Earth and Mars is a cornerstone of space exploration and scientific inquiry. The elliptical orbits of these planets mean that the distance between them is constantly changing, creating unique challenges for space missions, communication, and the potential for human colonization. This dynamic relationship between the two planets is a critical factor in planning and executing successful missions to Mars.
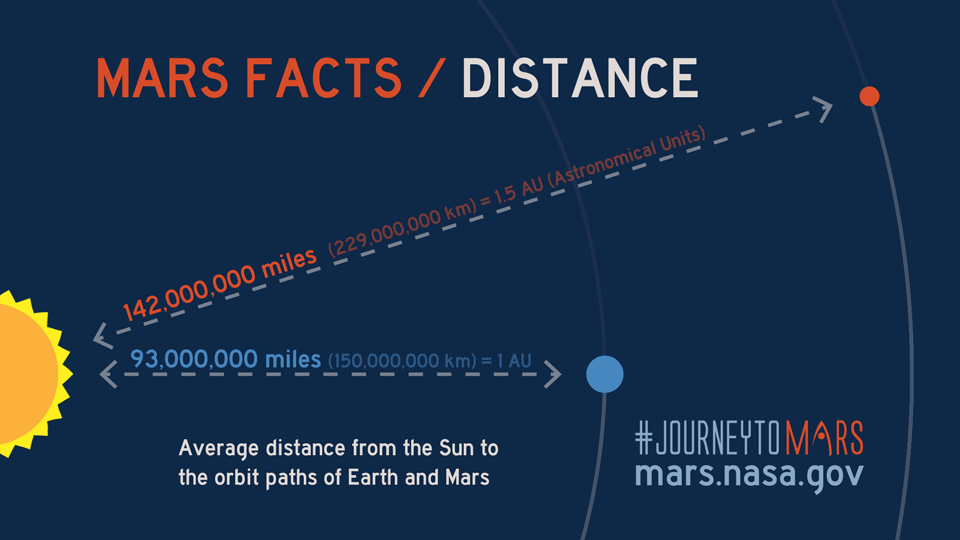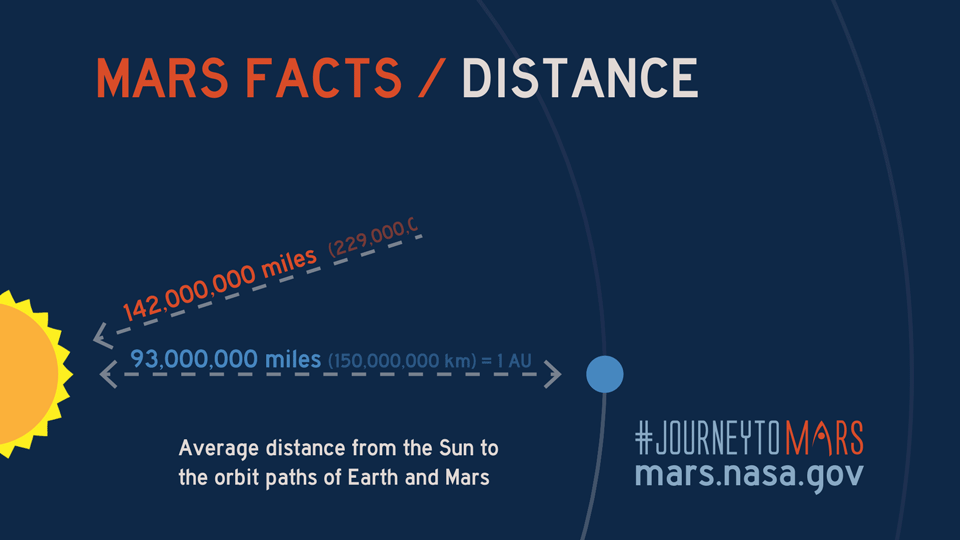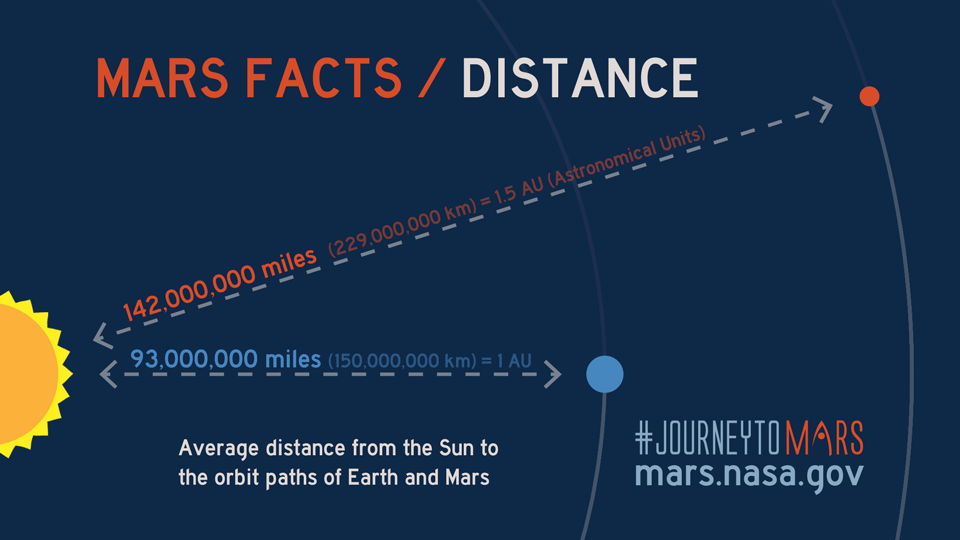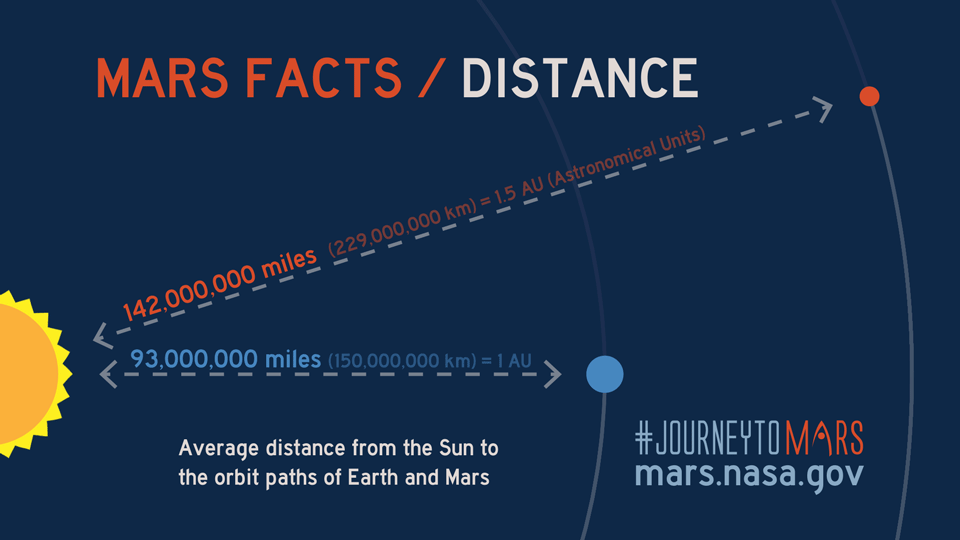
On average, the distance between Earth and Mars is approximately 225 million kilometers (140 million miles). However, this figure can vary widely depending on the relative positions of the planets in their orbits. The closest approach, known as opposition, occurs roughly every 26 months, while the farthest distance, called conjunction, happens when the planets are positioned on opposite sides of the Sun. These variations have profound implications for space exploration.
Scientists employ advanced telescopes and spacecraft to measure these distances with remarkable precision. These measurements are vital for mission planning, spacecraft design, and ensuring the safety of astronauts. The study of Earth-Mars distance is an integral part of modern astronomy, providing valuable insights into the workings of our solar system.
- Road Closures In Kansas
- Deandre Hopkins Height Weight
- Amazon Prime Call Center
- Charlieheen Ashton Kutcher
- Hilton Hotels On Duvaltreet Key West
The Orbital Mechanics of Earth and Mars
Both Earth and Mars follow elliptical orbits around the Sun, with Earth completing one orbit in about 365.25 days and Mars taking approximately 687 Earth days. This difference in orbital periods results in the distance between the two planets changing continuously, presenting both opportunities and challenges for space exploration.
Elliptical Orbits and Their Influence
The elliptical nature of the orbits means that the distance between Earth and Mars is not constant. When the planets are at their closest point, known as perihelion, and at their farthest point, called aphelion, the distance between them varies significantly. These variations are crucial for planning space missions, as they determine the optimal launch windows and mission durations.
- Earth's orbit is nearly circular, with a minor eccentricity of 0.0167.
- Mars has a more elliptical orbit, with an eccentricity of 0.0934.
- The difference in eccentricity affects the distance between the two planets, influencing mission planning and execution.
Understanding the Fluctuating Distance from Earth to Mars
The distance between Earth and Mars is subject to considerable variation due to their relative positions within the solar system. At its closest point, Mars is approximately 54.6 million kilometers (33.9 million miles) away from Earth, while at its farthest, the distance increases to about 401 million kilometers (249 million miles). These variations have significant implications for space missions and exploration efforts.
Factors Contributing to Distance Variations
Several factors contribute to the variations in the distance between Earth and Mars:
- The orbital eccentricity of both planets, which determines how elongated their orbits are.
- The relative speed and position of the planets in their orbits, which influence the timing and duration of missions.
- Gravitational influences from other celestial bodies, which can affect the trajectories of both planets.
These factors make predicting the exact distance at any given time a complex task. Astronomers use advanced calculations and simulations to determine the precise distance between Earth and Mars, ensuring that missions are planned with the utmost accuracy.
The Phenomenon of Mars' Closest Approach to Earth
One of the most exciting events in the study of Mars is its closest approach to Earth, known as opposition. This occurs when Mars and the Sun are on directly opposite sides of Earth, making Mars appear brighter and larger in the night sky. This event happens approximately every 26 months and provides a unique opportunity for observing and studying Mars in greater detail.
Notable Close Approaches in History
Some of the most remarkable close approaches of Mars to Earth include:
- 2003: Mars came within 55.76 million kilometers (34.65 million miles) of Earth, the closest it had been in nearly 60,000 years.
- 2018: Another close approach occurred, with Mars at a distance of 57.6 million kilometers (35.8 million miles).
These events are eagerly anticipated by astronomers and space enthusiasts worldwide, as they offer unparalleled opportunities for observation and data collection.
Navigating Mars' Farthest Distance from Earth
At its farthest point, Mars is located on the opposite side of the Sun from Earth, a position known as solar conjunction. During this time, the distance between the two planets can reach up to 401 million kilometers (249 million miles). This vast distance poses significant challenges for communication with spacecraft on Mars, as the Sun's intense radiation can interfere with radio signals.
Challenges Posed by Solar Conjunction
During solar conjunction, the Sun's radiation can disrupt communication between Earth and Mars, necessitating a temporary pause in interactions with spacecraft on the planet. NASA and other space agencies carefully plan for this period to ensure the safety and functionality of their missions. This planning involves pre-programming spacecraft to operate autonomously during the conjunction and resuming communication once the period has passed.
The Journey from Earth to Mars: A Closer Look
The duration of a journey from Earth to Mars depends on several factors, including the relative positions of the planets, the type of spacecraft used, and the mission objectives. On average, a trip to Mars takes about six to nine months using current technology. This time frame is influenced by the launch window, spacecraft design, and mission priorities.
Factors Influencing Travel Time
- Launch window: The optimal time for launching a spacecraft to Mars occurs every 26 months, aligning with the planets' closest approach.
- Spacecraft design: The speed and efficiency of the spacecraft play a critical role in determining travel time.
- Mission objectives: Some missions prioritize speed, while others focus on conducting extensive scientific research during the journey.
Advancements in propulsion technology hold the promise of significantly reducing travel time, making Mars exploration more efficient and accessible in the future.
A Legacy of Space Missions to Mars
Since the 1960s, numerous space missions have been launched to study Mars, providing invaluable insights into the planet's atmosphere, geology, and potential for supporting life. These missions have paved the way for our current understanding of Mars and the challenges of exploring it. Some of the most notable missions include:
- Mariner 4 (1965): The first successful flyby of Mars, providing the first close-up images of the planet's surface.
- Viking 1 and 2 (1976): The first successful landings on Mars, conducting groundbreaking experiments to search for signs of life.
- Mars Rover missions (Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, Perseverance): These rovers have explored the Martian surface extensively, uncovering critical information about the planet's history and potential habitability.
Each mission has contributed to our growing knowledge of Mars, highlighting the importance of continued exploration and research.
Conquering the Technological Hurdles of Mars Exploration
Mars exploration presents a myriad of technological challenges that require innovative solutions. The vast distance between Earth and Mars, combined with the planet's harsh conditions, demands cutting-edge technology and engineering expertise. Key challenges include:
- Communication delays: Signals take between 4 and 24 minutes to travel between Earth and Mars, complicating real-time interactions.
- Surviving extreme temperatures: Mars experiences temperatures as low as -80 degrees Fahrenheit (-62 degrees Celsius), requiring robust systems to withstand these conditions.
- Developing sustainable life support systems: Future missions will need advanced systems for producing air, water, and food to support human life on the planet.
Ongoing research and development efforts aim to overcome these challenges, paving the way for successful human exploration of Mars and beyond.
The Future of Mars Exploration: Ambitious Plans and Collaborations
The future of Mars exploration is filled with promise, with several ambitious initiatives underway. NASA's Artemis program aims to return humans to the Moon as a stepping stone for Mars missions, while SpaceX's Starship project envisions sending humans to Mars within the next decade. These efforts reflect the growing interest in Mars exploration and the potential for human colonization.
The Role of International Collaboration
International collaboration plays a vital role in advancing Mars exploration. By pooling resources, knowledge, and technology, countries and organizations worldwide are working together to ensure that future missions are safe, efficient, and scientifically rewarding. This collaborative approach underscores the global commitment to unraveling the mysteries of Mars and expanding humanity's presence in the cosmos.
Summing Up: The Importance of Understanding Earth-Mars Distance
In summary, understanding the distance between Earth and Mars is crucial for space exploration and scientific research. The dynamic nature of this distance, influenced by the elliptical orbits of both planets, has significant implications for mission planning, communication, and the feasibility of human colonization. Through ongoing research and technological advancements, humanity is making remarkable progress in exploring and understanding Mars.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. For more in-depth articles on space exploration and astronomy, explore our website. Together, let's continue to unlock the secrets of the universe and inspire future generations to reach for the stars!


Detail Author:
- Name : Santino Rohan
- Username : torrey.cruickshank
- Email : haley.ankunding@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1978-06-22
- Address : 479 Otilia Coves Apt. 612 Nikolausfort, TX 52394
- Phone : +19299294528
- Company : Champlin, Schoen and Frami
- Job : Streetcar Operator
- Bio : Commodi est quisquam sed voluptas. Ea eum sed ut ut quia nobis delectus autem. Cum nisi alias libero voluptas nulla nisi.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/kevon5545
- username : kevon5545
- bio : Non id dolor dolore itaque molestias. Debitis repellat porro accusamus et. Minus quia quisquam similique. Sed nihil perferendis dicta.
- followers : 3983
- following : 2332
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/kevon5954
- username : kevon5954
- bio : Unde qui hic fugit non unde eos voluptas.
- followers : 1023
- following : 726
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/schmidt2012
- username : schmidt2012
- bio : Consequatur pariatur est aut est.
- followers : 6152
- following : 129