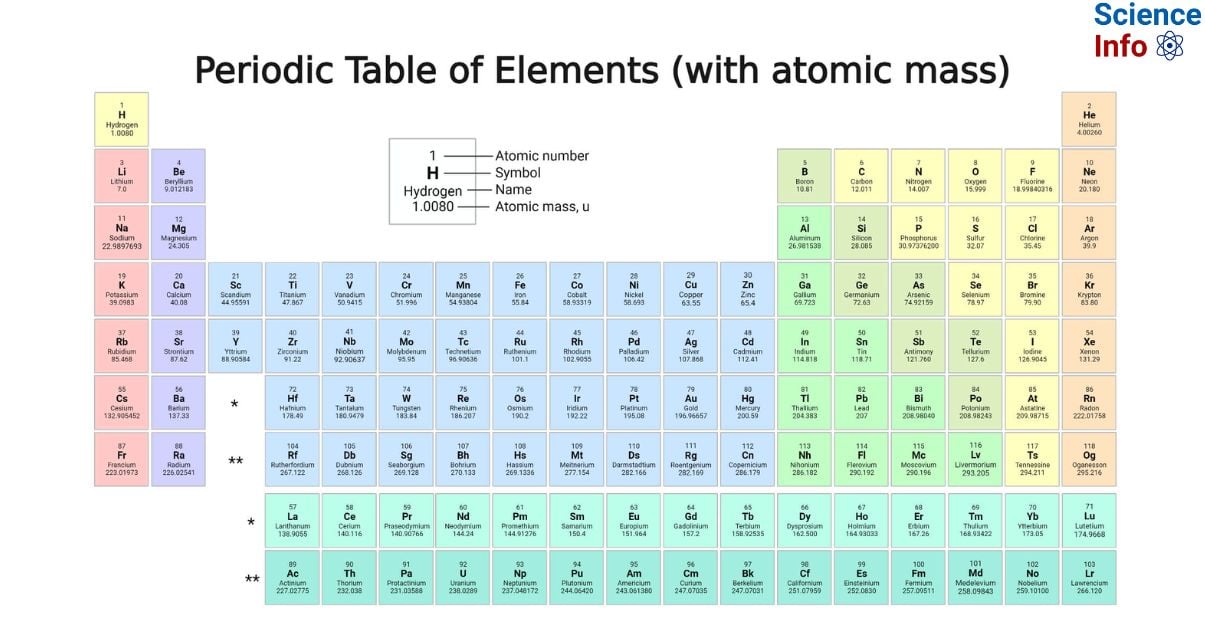
The periodic table, which includes atomic mass, is a cornerstone of chemistry and physics. It provides critical information about the structure and properties of elements, enabling scientists to conduct precise calculations and understand the interactions between elements. By studying the periodic table, we can uncover valuable insights into the nature of matter and how elements behave under different conditions.
The periodic table is far from a random collection of elements; it is a meticulously organized chart that reveals the periodic trends and properties of all known elements. Grasping the concept of atomic mass is essential for anyone with an interest in science, as it underpins many chemical reactions and physical phenomena that shape our world.
This article offers an in-depth exploration of the periodic table, focusing on atomic mass, its structure, significance, and applications. Whether you are a student, educator, or science enthusiast, this guide will deepen your understanding of atomic mass and its pivotal role in modern science.
- Donald Trump Children Names
- When Did Bob Marley Die Age
- Outlet Centermithfield Nc
- Alice Braga Moraes
- Calling Amazon
Table of Contents
- Evolution of the Periodic Table
- What is Atomic Mass?
- Periodic Trends in Atomic Mass
- How Atomic Mass Affects Element Properties
- The Role of Isotopes in Atomic Mass
- Practical Applications of Atomic Mass
- Calculating Atomic Mass
- Understanding Mass Spectra
- Future Developments in the Periodic Table
- Final Thoughts
Evolution of the Periodic Table
The periodic table has a fascinating history that traces back to the 19th century. Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, is credited with creating the first periodic table in 1869. His groundbreaking work systematically organized elements based on their atomic weights and chemical properties. Mendeleev's table was revolutionary not only for its organization but also for its predictive power—it anticipated the existence of undiscovered elements, which were later confirmed through scientific research.
Over time, the periodic table has undergone significant transformations. The modern periodic table is now based on atomic numbers rather than atomic weights, offering a more precise representation of the elements. This evolution has deepened our understanding of periodic trends and relationships among elements, including their atomic masses, and has become an indispensable tool for scientists worldwide.
What is Atomic Mass?
Atomic mass refers to the total mass of an atom, primarily determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Measured in atomic mass units (amu), atomic mass is a fundamental parameter in both chemistry and physics. In the periodic table, the atomic mass of an element is typically listed below its symbol, providing a quick reference for scientists and students alike.
- Amc Independence Commons 20 Theater
- Quality Inn Hotel Ocean City Md
- Billings Mt
- Welsh Park Rockville Md
- Cinema West Hartford
Variations in Atomic Mass
While the atomic mass of an element is generally consistent, variations can occur due to the presence of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons, which can lead to variations in atomic mass. Recognizing and accounting for these variations is crucial for ensuring accurate scientific calculations and analyses.
Periodic Trends in Atomic Mass
The periodic table displays several trends related to atomic mass. As you move across a period from left to right, the atomic mass generally increases due to the addition of protons and neutrons. Similarly, as you move down a group, the atomic mass tends to increase because of the growing number of electron shells. These trends play a critical role in predicting how elements will behave in various chemical reactions and interactions.
Understanding these periodic trends is essential for scientists who need to make informed decisions about the compatibility and reactivity of different elements. By analyzing these trends, researchers can anticipate the behavior of elements in diverse chemical environments, enabling them to design experiments and applications with greater precision.
How Atomic Mass Affects Element Properties
Atomic mass significantly influences the physical and chemical properties of elements. For example, elements with higher atomic masses often exhibit greater density and higher melting and boiling points. Furthermore, atomic mass plays a key role in determining the reactivity of elements, particularly in reactions involving ions and molecules. This relationship between atomic mass and element properties is vital for understanding the behavior of matter at the atomic level.
Key Properties Influenced by Atomic Mass
- Density
- Melting and boiling points
- Reactivity
- Electron affinity
The Role of Isotopes in Atomic Mass
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons, leading to variations in atomic mass. These variations are reflected in the average atomic mass listed in the periodic table, which represents a weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. Understanding isotopes is critical in fields such as nuclear physics, where they are utilized in various applications, including power generation and medical imaging.
The study of isotopes also provides valuable insights into the origins of elements and the processes that govern their formation. By examining isotopic compositions, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the universe's history and the mechanisms that drive element creation.
Practical Applications of Atomic Mass
The concept of atomic mass has far-reaching practical applications across numerous fields. Below are some of the most significant areas where atomic mass plays a crucial role:
Applications in Chemistry
In chemistry, atomic mass is indispensable for calculating the molar mass of compounds, a fundamental aspect of stoichiometric calculations. This enables chemists to determine the precise amounts of reactants and products in chemical reactions, ensuring accuracy and reliability in laboratory experiments and industrial processes.
Applications in Physics
In physics, atomic mass is essential for studying the behavior of atomic nuclei and the energy released during nuclear reactions. This knowledge is applied in the development of nuclear power plants and atomic weapons, as well as in advancing our understanding of the universe's fundamental forces.
Applications in Medicine
In medicine, isotopes are widely used in diagnostic imaging and cancer treatment. Radioactive isotopes emit radiation that can be detected by imaging equipment, allowing doctors to visualize internal structures and diagnose diseases with remarkable precision. Additionally, isotopes are employed in radiation therapy to target and destroy cancer cells, offering hope to patients worldwide.
Calculating Atomic Mass
Calculating atomic mass involves determining the weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. This calculation takes into account the relative abundance of each isotope, ensuring an accurate and comprehensive representation of the element's atomic mass.
Formula for Calculating Atomic Mass:
Atomic Mass = (Mass of Isotope 1 × Abundance of Isotope 1) + (Mass of Isotope 2 × Abundance of Isotope 2) + ...
Understanding Mass Spectra
A mass spectrum is a graphical representation of the masses of ions produced during a mass spectrometry analysis. It provides crucial information about the atomic and molecular composition of a sample, including the presence of isotopes and their relative abundances. Mass spectrometry is widely used in fields such as chemistry, biology, and environmental science to analyze complex mixtures and identify unknown compounds.
The data obtained from mass spectrometry can be used to calculate atomic masses and study the behavior of elements in various environments, making it an invaluable tool for researchers across multiple disciplines.
Future Developments in the Periodic Table
As scientific research continues to progress, the periodic table is likely to evolve further. The discovery of new elements and isotopes will expand our understanding of atomic mass and its implications. Moreover, advancements in technology may introduce novel methods for studying and analyzing the properties of elements, offering even deeper insights into their behavior.
Scientists are also exploring the potential for creating synthetic elements with unique properties, which could transform various industries. These developments underscore the importance of the periodic table as a dynamic and evolving resource in the field of science.
Final Thoughts
The periodic table, with its focus on atomic mass, is an indispensable resource for anyone with an interest in science. By comprehending the atomic mass of elements and their periodic trends, we gain profound insights into the fundamental building blocks of matter and their interactions. This knowledge has countless applications in fields such as chemistry, physics, and medicine, driving innovation and progress in countless ways.
We encourage readers to delve deeper into the periodic table and apply its principles in their studies and research. Feel free to share your thoughts, comments, or questions below, and don't hesitate to share this article with others who may find it beneficial. For more information on related topics, explore our other articles on this website.


Detail Author:
- Name : Leone Champlin
- Username : rortiz
- Email : shirley09@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 2005-10-05
- Address : 261 Wade Prairie West Camden, MD 17102-4965
- Phone : +1-909-941-9066
- Company : Beatty, O'Kon and Kuhlman
- Job : Broadcast News Analyst
- Bio : Velit possimus doloribus est. Qui ullam ratione repellat ratione. Ut ut hic est aliquam quod. Est recusandae laborum sit corporis sequi.
Socials
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@ulices9383
- username : ulices9383
- bio : Perspiciatis dolore aliquid qui. Perferendis aliquam sit aut vel harum.
- followers : 750
- following : 2471
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/ulices.anderson
- username : ulices.anderson
- bio : Numquam animi eius fugiat porro doloribus.
- followers : 1148
- following : 2335