The evolution of cars is a remarkable testament to human creativity and technological advancement. From the early days of self-propelled vehicles to the modern era of electric and autonomous cars, this journey has profoundly influenced the world we live in today. Delving into the history of automobiles provides a deeper understanding of how transportation became a fundamental pillar of modern society.
Over the centuries, cars have not only revolutionized the way people move but also had a significant impact on economies, cultures, and everyday life. This article will guide you through the pivotal moments in the development of automobiles, shining a light on the inventors, innovations, and societal transformations that have shaped the automotive industry.
Whether you're a passionate car enthusiast or simply intrigued by the origins of this groundbreaking invention, this detailed exploration will take you on a chronological voyage through the history of automobiles. Let's embark on this fascinating journey and uncover the story behind one of humanity's most remarkable achievements.
- How Old Vince Gill
- Mastiff Mix Dogs
- Calling Amazon
- Nate Robinson Draft Pick
- Koa Campground Near Dollywood
Table of Contents
- The Dawn of Self-Propelled Vehicles
- The Industrial Revolution and Steam-Powered Cars
- The Breakthrough of the Internal Combustion Engine
- Henry Ford and the Assembly Line Transformation
- The Post-War Boom: Expansion and Innovation
- The Oil Crisis and the Drive for Fuel Efficiency
- Environmental Concerns and the Rise of Hybrid Vehicles
- The Rise of Electric Vehicles
- The Future of Autonomous Vehicles
- Conclusion: A Legacy of Progress
The Dawn of Self-Propelled Vehicles
The concept of self-propelled vehicles dates back centuries before the first functional car was ever constructed. Visionaries and engineers embarked on a quest to create machines capable of moving without reliance on human or animal power. One of the earliest examples comes from Leonardo da Vinci, whose sketches in the 15th century depicted designs for self-moving carts that, although never built during his lifetime, laid the groundwork for future innovations.
Key Innovations in Early Transportation
In the 17th century, the Flemish engineer Ferdinand Verbiest created a miniature steam-powered vehicle for the Chinese emperor, marking one of the first attempts at developing a self-propelled machine. Although impractical for everyday use, this invention showcased the potential of steam power in transportation. A few centuries later, in 1769, Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot introduced the first full-scale steam-powered car in France, setting the stage for further advancements.
- 1672: Ferdinand Verbiest designs a steam-powered vehicle for the Chinese court.
- 1769: Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot develops the first full-scale steam-powered car in France.
The Industrial Revolution and Steam-Powered Cars
The Industrial Revolution of the late 18th and early 19th centuries ushered in a wave of engineering and manufacturing breakthroughs. Steam power, which had already transformed industries such as textiles and mining, began to be applied to transportation. Inventors like Richard Trevithick and Goldsworthy Gurney developed steam-powered carriages capable of carrying passengers and goods over long distances.
- The Tides Monterey Ca
- Billings Mt
- Welsh Park Rockville Md
- Millbutn Deli
- The Lemont Restaurant Pittsburgh
Challenges of Steam-Powered Vehicles
Despite their promise, steam-powered cars faced numerous challenges, including limited range, slow acceleration, and the need for frequent refueling. Additionally, the bulkiness and weight of steam engines made them impractical for widespread adoption. Nevertheless, these early experiments paved the way for future innovations in automotive technology, showcasing the resilience and determination of early inventors.
The Breakthrough of the Internal Combustion Engine
The invention of the internal combustion engine marked a pivotal moment in the history of automobiles. German engineers Nikolaus Otto and Gottlieb Daimler developed the first practical gasoline-powered engines in the late 19th century. These engines were lighter, more efficient, and easier to operate than their steam-powered predecessors.
Key Milestones in Engine Development
- 1876: Nikolaus Otto patents the groundbreaking four-stroke internal combustion engine.
- 1886: Karl Benz constructs the first gasoline-powered car, the Benz Patent-Motorwagen, revolutionizing personal transportation.
The introduction of the internal combustion engine opened the door to mass production of automobiles, making them accessible to a wider audience and setting the stage for the modern automotive industry.
Henry Ford and the Assembly Line Transformation
In 1913, Henry Ford revolutionized the automotive industry by introducing the moving assembly line. By optimizing the production process, Ford drastically reduced the time and cost of manufacturing cars, making them affordable for the average consumer. The Model T, unveiled in 1908, became a symbol of this new era of mass-produced automobiles, transforming the way people traveled and lived.
The Impact of Ford's Innovations
Ford's assembly line not only reshaped the car industry but also influenced manufacturing practices across various sectors. It led to increased efficiency, lower prices, and greater accessibility of goods for consumers worldwide. By 1927, over 15 million Model T cars had been produced, cementing Ford's status as a pioneer in automotive innovation and leaving an indelible mark on industrial history.
The Post-War Boom: Expansion and Innovation
Following World War II, the global demand for automobiles surged as economies recovered and suburbanization expanded. Manufacturers responded by diversifying their offerings, introducing new models and features to meet the evolving needs of consumers. This period also witnessed the rise of iconic brands such as Chevrolet, Volkswagen, and Toyota, which gained worldwide recognition for their quality and innovation.
Trends in Post-War Car Design
Post-war car designs embodied the optimism and prosperity of the era, featuring sleek lines, chrome accents, and powerful engines. In response to growing concerns about road safety, features such as seat belts and padded dashboards began to appear. Additionally, compact cars were introduced to cater to urban drivers and fuel-conscious consumers, reflecting the changing priorities of the time.
The Oil Crisis and the Drive for Fuel Efficiency
The oil crisis of the 1970s forced automakers to rethink their approach to car design and production. Rising fuel prices and dwindling resources prompted consumers to demand more fuel-efficient vehicles. Japanese manufacturers, such as Toyota and Honda, capitalized on this trend by offering compact, reliable cars that delivered exceptional mileage, setting new standards for the industry.
Technological Responses to the Oil Crisis
- Development of smaller, more efficient engines to reduce fuel consumption.
- Introduction of catalytic converters to minimize emissions and promote environmental responsibility.
- Increased investment in research and development of alternative fuels to explore sustainable solutions.
These innovations not only addressed immediate concerns but also laid the foundation for future advancements in automotive technology, showcasing the adaptability of the industry.
Environmental Concerns and the Rise of Hybrid Vehicles
As environmental awareness grew in the late 20th century, automakers began exploring ways to reduce the environmental impact of cars. Hybrid vehicles, which combine gasoline engines with electric motors, emerged as a practical solution. Toyota's Prius, introduced in 1997, became the world's first mass-produced hybrid car, setting a new benchmark for fuel efficiency and eco-friendliness.
Benefits of Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid vehicles offer numerous advantages, including:
- Improved fuel efficiency, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Reduced emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier planet.
- Enhanced driving experience through advanced technology, such as regenerative braking and intelligent energy management systems.
The Rise of Electric Vehicles
The 21st century has witnessed a dramatic surge in the development and adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). Companies like Tesla, Nissan, and Chevrolet have introduced EVs that combine cutting-edge technology with stylish designs and impressive performance. Government incentives and growing consumer awareness of environmental issues have further accelerated the shift toward electric transportation, marking a new era in automotive history.
Key Advantages of Electric Vehicles
- Zero tailpipe emissions, promoting cleaner air and a more sustainable future.
- Lower operating costs compared to gasoline-powered cars, providing long-term financial benefits.
- Access to advanced features such as autonomous driving capabilities, enhancing the driving experience.
The Future of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles represent the next frontier in automotive innovation. Companies like Waymo, Tesla, and Uber are investing heavily in research and development to bring self-driving cars to market. While challenges remain in terms of technology, regulation, and public acceptance, the potential benefits of autonomous vehicles are vast, promising to transform the way we travel.
Potential Impact of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous cars have the potential to revolutionize transportation by offering:
- Enhanced safety through advanced sensors and artificial intelligence systems, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Increased productivity by allowing drivers to focus on other tasks during commutes, maximizing their time.
- Environmental benefits through optimized routes and reduced fuel consumption, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Progress
The history of automobiles is a powerful testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of progress. From the early experiments with steam-powered vehicles to the cutting-edge innovations of electric and autonomous cars, the automotive industry has continually evolved to meet the changing needs of society.
As we look to the future, it is evident that cars will continue to play a vital role in shaping the world. By embracing sustainable practices and advancing technology, we can ensure that the legacy of automotive innovation endures for generations to come.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments below. Have you experienced any of the milestones mentioned in this article? What do you envision for the future of the automotive industry? Don't forget to explore other articles on our site for more engaging content!
Data and references for this article were sourced from reputable publications such as History.com, Encyclopedia Britannica, and Tesla's official website.
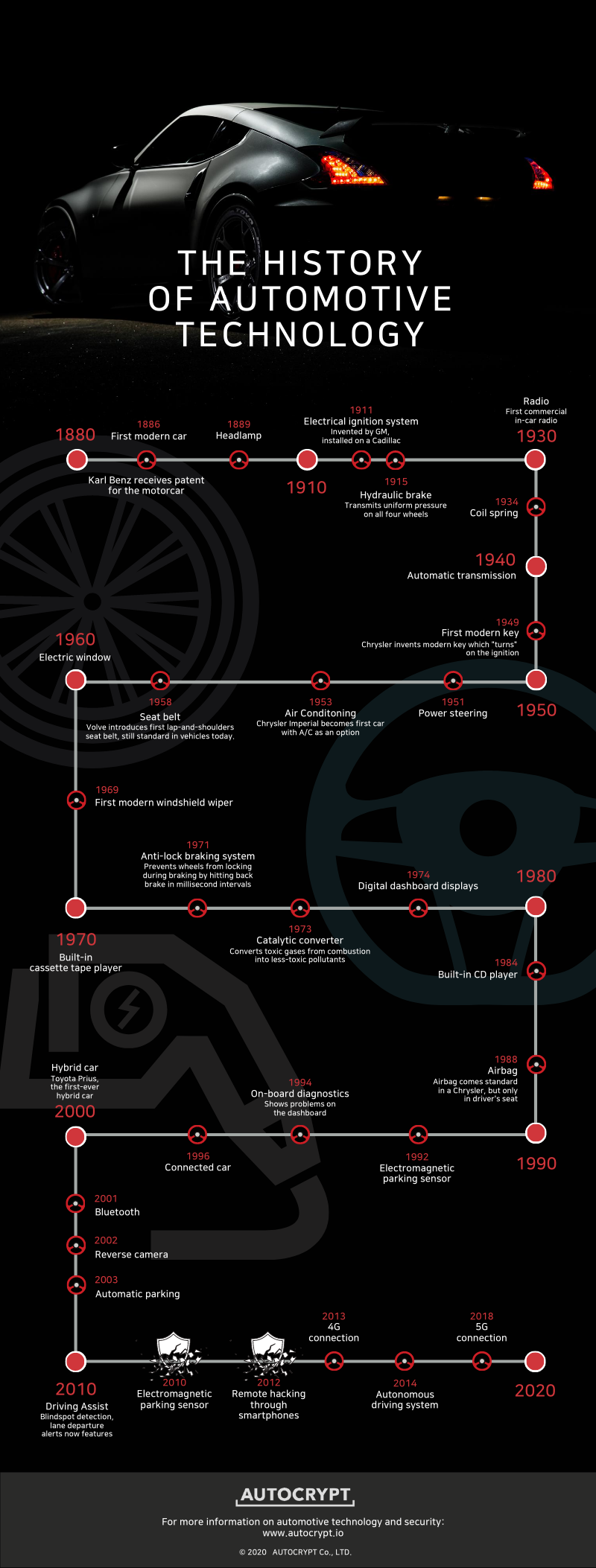
![Timeline A History of Car Technology [INFOGRAPHIC]](http://infographicplaza.com/wp-content/uploads/car-technology-timeline-infographic-plaza.jpg)

Detail Author:
- Name : Marlon Rippin
- Username : ron.lebsack
- Email : kschimmel@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1979-05-21
- Address : 91465 Neil Brook Apt. 946 Raynorshire, DE 96506
- Phone : +1-480-582-1919
- Company : Stroman Ltd
- Job : Archivist
- Bio : Earum odit recusandae aut reprehenderit. Odit velit ex velit voluptatem tempore id. Quo quia sequi ipsum. Eius sunt sint eveniet voluptatem aut nemo ea sed.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/reicherte
- username : reicherte
- bio : Nostrum qui dolores voluptate ut.
- followers : 2593
- following : 1616
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/elinor_reichert
- username : elinor_reichert
- bio : In labore nihil sapiente. Dolores ad qui omnis inventore deleniti repudiandae.
- followers : 5880
- following : 460