Choosing the right partition style is crucial for how your computer manages and organizes data. Whether you're setting up a new system or troubleshooting an existing one, understanding the differences between GUID Partition Table (GPT) and Master Boot Record (MBR) is essential for ensuring optimal performance and security. Both partition types offer unique advantages, but selecting the one that aligns with your specific needs can significantly enhance your computing experience.
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the demand for efficient and flexible storage solutions continues to rise. GPT and MBR are two of the most popular partitioning systems available, each tailored to distinct scenarios. This guide will explore the intricacies of both partition types, helping you make an informed decision that best suits your requirements.
By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of the differences between GPT and MBR, their respective features, limitations, and how to determine which one is the right fit for your system. Let's begin!
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Partition Types
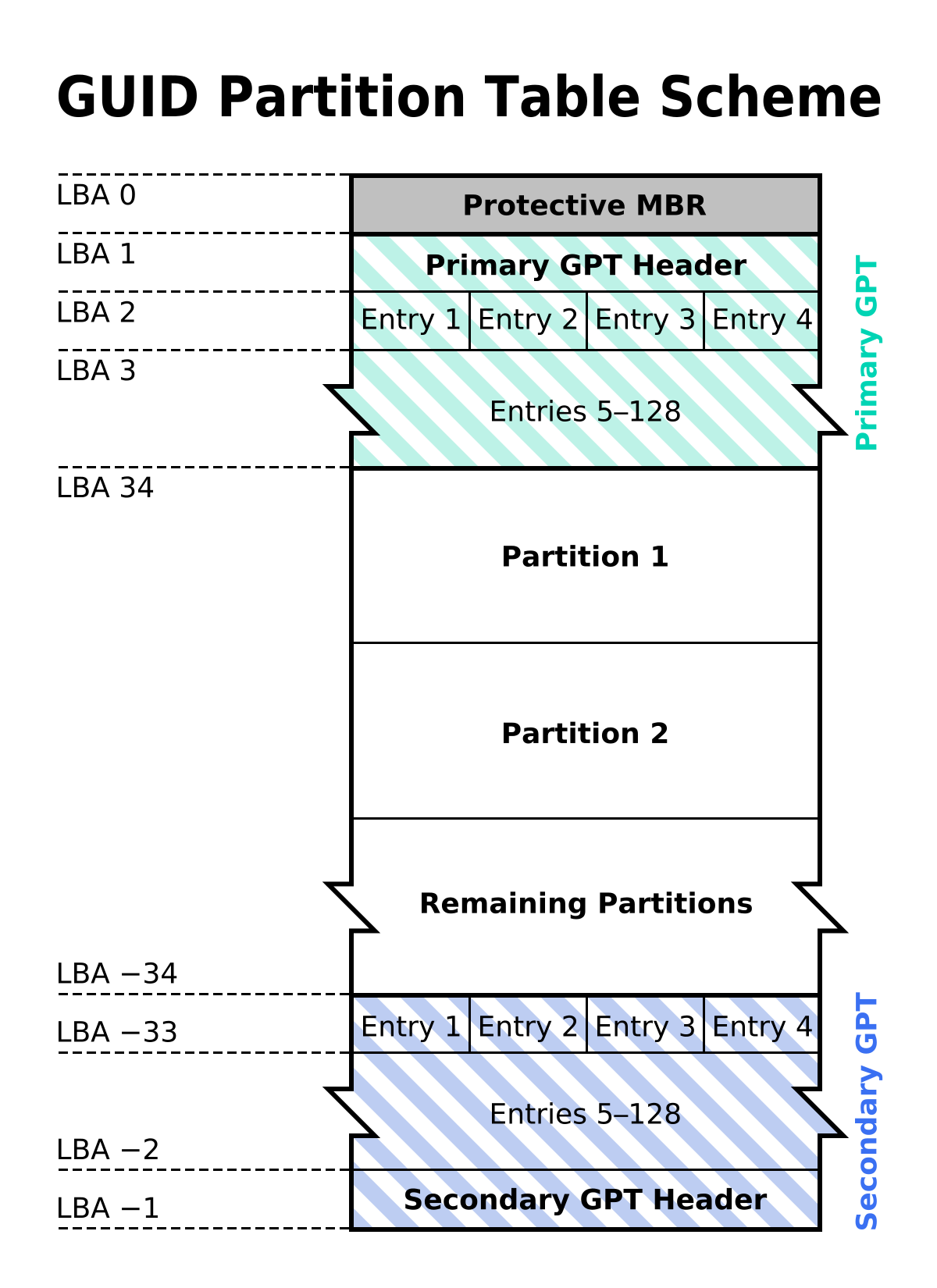
- What is GPT Partition?
- What is MBR Partition?
- Key Differences Between GPT and MBR
- Compatibility Considerations
- Performance Comparison
- Security Features
- How to Convert MBR to GPT
- Common Questions About Partitions
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding Partition Types: Why They Matter
Before delving into the specifics of GPT versus MBR, it's essential to grasp the concept of partitioning and its significance in data management. A partition essentially divides a hard drive or solid-state drive (SSD) into distinct logical sections, enabling better organization of data and improved system performance. This segmentation allows users to allocate specific sections for operating systems, applications, and personal files, streamlining the overall functioning of the computer.
There are two primary partitioning methods: Master Boot Record (MBR) and GUID Partition Table (GPT). Each method has its own set of strengths and limitations, making them suitable for different types of systems and use cases. Understanding the nuances of these partition styles will empower you to make the most appropriate choice for your computing environment.
Exploring GPT Partition: The Modern Solution
GUID Partition Table (GPT) represents a cutting-edge partitioning system that was introduced alongside the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard. It offers several advantages over the traditional MBR system, particularly in terms of scalability, reliability, and security. GPT has become the preferred choice for modern systems due to its ability to accommodate large drives and provide robust data protection mechanisms.
Some of the standout features of GPT partitions include:
- Unlimited Drive Size Support: GPT can handle drives with capacities exceeding 2TB, a limitation that MBR cannot overcome. This makes GPT ideal for high-capacity storage devices such as SSDs and HDDs.
- Enhanced Partitioning Flexibility: With GPT, you can create up to 128 primary partitions, whereas MBR restricts you to just four. This flexibility allows for more granular data organization and management.
- Improved Data Integrity: GPT incorporates redundant backup tables, ensuring that even if the primary partition table becomes corrupted, the backup can restore the original configuration, minimizing the risk of data loss.
MBR Partition: The Legacy Option
Master Boot Record (MBR) has been the standard partitioning method for decades, widely supported across older systems. While it remains a reliable choice for legacy setups, its limitations become apparent when dealing with modern, high-capacity drives. Despite its shortcomings, MBR continues to serve as a practical solution for specific scenarios.
Key characteristics of MBR partitions include:
- 2TB Capacity Limitation: MBR cannot support drives larger than 2TB, which may pose challenges for users requiring extensive storage solutions.
- Restricted Partitioning Options: MBR allows for a maximum of four primary partitions, or three primary partitions combined with one extended partition. This restriction can limit data organization capabilities.
- Extensive Legacy Support: MBR is compatible with a wide range of older operating systems and hardware, making it a suitable option for users working with outdated systems.
Key Differences Between GPT and MBR Partitioning
Storage Capacity: A Major Distinction
One of the most notable distinctions between GPT and MBR lies in their capacity to handle large storage drives. GPT supports drives with sizes up to an impressive 9.4 zettabytes (ZB), while MBR is constrained to a maximum of 2TB. This capability makes GPT the go-to choice for modern systems equipped with high-capacity SSDs and HDDs, ensuring they can fully utilize the available storage space.
Data Recovery: Enhanced Protection with GPT
GPT's design includes a backup partition table located at the end of the drive, providing a critical safeguard against data loss. In the event that the primary partition table becomes corrupted, the backup table can be utilized to restore the original configuration. Conversely, MBR lacks this redundancy feature, making data recovery more challenging and less reliable.
Compatibility Considerations: Matching Partition Style to Your System
When deciding between GPT and MBR, compatibility plays a pivotal role. GPT is predominantly employed in systems utilizing UEFI firmware, while MBR is more prevalent in BIOS-based systems. If you're working with an older system or require booting from a USB drive on a legacy machine, MBR may be the more suitable option.
However, modern systems increasingly support both UEFI and BIOS, offering greater flexibility in partitioning choices. It's crucial to review your system specifications and firmware settings before making a decision to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance.
Performance Comparison: Beyond Partitioning
In terms of raw performance, GPT and MBR exhibit comparable results. The primary performance enhancements typically stem from utilizing modern hardware and optimized file systems rather than the partitioning scheme itself. Nevertheless, GPT's ability to manage larger drives and accommodate more partitions can lead to improved organization and potentially better performance in specific scenarios.
Security Features: Why GPT Stands Out
GPT boasts several security advantages over MBR, enhancing its appeal for systems requiring heightened protection. Its use of Globally Unique Identifiers (GUIDs) for partitions renders it more resilient against corruption and unauthorized access. Moreover, the redundant backup tables provide an additional layer of defense against data loss, making GPT a preferred choice for enterprise servers and personal computers storing sensitive information.
For systems where security is a top priority, GPT offers a more robust and reliable solution compared to its predecessor.
Converting MBR to GPT: A Step-by-Step Guide
Transitioning from MBR to GPT can be a straightforward process, provided you approach it with careful planning to prevent data loss. Follow these steps to convert your MBR partition to GPT:
- Backup Your Data: Before proceeding, ensure all important data is securely backed up to avoid any potential loss during the conversion process.
- Use Disk Management Tools: Utilize a reliable disk management utility such as Diskpart in Windows or GParted in Linux to perform the conversion.
- Verify Firmware Compatibility: Confirm that your system firmware (BIOS/UEFI) supports GPT to ensure smooth operation after the conversion.
- Reinstall the Operating System if Necessary: Some older operating system versions may not support GPT, necessitating a reinstallation to ensure compatibility.
Always refer to the official documentation for your operating system and hardware to ensure a successful and secure conversion.
Common Questions About GPT and MBR Partitions
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about GPT and MBR partitions:
- Can I Use Both GPT and MBR on the Same System? No, a single disk can only utilize one partition style. However, you can employ multiple disks with different partition schemes to meet your specific needs.
- Is GPT Faster Than MBR? While GPT and MBR exhibit similar performance levels, GPT offers superior scalability and reliability, making it a more future-proof choice for modern systems.
- Do I Need UEFI to Use GPT? Although UEFI is strongly recommended for GPT, some systems can boot GPT drives in BIOS mode using a compatibility layer, providing additional flexibility.
Conclusion and Next Steps: Making the Right Choice
In summary, both GPT and MBR partition styles offer distinct advantages and limitations, catering to different types of systems and use cases. GPT has emerged as the preferred option for modern systems due to its ability to support large drives, enhanced data recovery capabilities, and superior security features. On the other hand, MBR remains a practical solution for legacy systems and specific scenarios where compatibility with older hardware and software is crucial.
To determine the best partition style for your system, consider factors such as drive size, compatibility requirements, and future upgrade plans. If you're uncertain, consulting with a professional or referring to the documentation for your hardware and operating system can provide valuable guidance.
We invite you to share your thoughts and feedback in the comments section below. If you found this article helpful, feel free to share it with others who may benefit from the information. Exploring our other articles on data management will further enhance your understanding and skills in this area. Your engagement and feedback help us improve and deliver better content for our audience.
Data Source: Microsoft Documentation, GNU Parted Manual


Detail Author:
- Name : Santino Rohan
- Username : torrey.cruickshank
- Email : haley.ankunding@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1978-06-22
- Address : 479 Otilia Coves Apt. 612 Nikolausfort, TX 52394
- Phone : +19299294528
- Company : Champlin, Schoen and Frami
- Job : Streetcar Operator
- Bio : Commodi est quisquam sed voluptas. Ea eum sed ut ut quia nobis delectus autem. Cum nisi alias libero voluptas nulla nisi.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/kevon5545
- username : kevon5545
- bio : Non id dolor dolore itaque molestias. Debitis repellat porro accusamus et. Minus quia quisquam similique. Sed nihil perferendis dicta.
- followers : 3983
- following : 2332
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/kevon5954
- username : kevon5954
- bio : Unde qui hic fugit non unde eos voluptas.
- followers : 1023
- following : 726
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/schmidt2012
- username : schmidt2012
- bio : Consequatur pariatur est aut est.
- followers : 6152
- following : 129