Aluminum, spelled as "aluminium" in certain regions, is one of the most versatile and widely utilized materials across numerous industries. Whether it's construction, automotive manufacturing, or aerospace engineering, this metal plays a pivotal role in modern innovation. Its lightweight nature, coupled with remarkable strength and corrosion resistance, makes it indispensable for a variety of applications. But what exactly is the difference between "aluminium" and "aluminum," and why does this distinction matter?
For many years, the debate surrounding the spelling of this metal has intrigued people globally. While some countries favor "aluminium," others opt for "aluminum." This article delves deeply into the intricacies of this material, exploring its properties, applications, historical background, and importance in contemporary industries. By the conclusion, readers will possess a thorough understanding of why both terms exist and how this material profoundly influences daily life.
From its initial discovery to its cutting-edge applications today, aluminum/aluminium continues to transform industries worldwide. Its adaptability and commitment to sustainability make it a preferred choice for engineers, architects, and manufacturers alike. Let’s journey into the fascinating world of aluminum/aluminium and uncover its significance.
Table of Contents
- The Evolution of Aluminum/Aluminium
- Key Properties of Aluminum/Aluminium
- Exploring the Spelling Variations
- Versatile Applications of Aluminum/Aluminium
- Environmental Considerations
- The Manufacturing Process
- Industries Benefiting from Aluminum/Aluminium
- Advantages of Aluminum/Aluminium
- Challenges in Aluminum/Aluminium Production
- The Future of Aluminum/Aluminium
The Evolution of Aluminum/Aluminium
Aluminum/aluminium's journey began in the early 19th century when Danish physicist Hans Christian Oersted successfully isolated the metal in 1825. This marked the inception of aluminum as a revolutionary material. However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that advancements in production techniques made aluminum commercially viable.
In the 1880s, the Hall-Héroult process was introduced, drastically reducing the cost of aluminum production. This electrolysis-based method enabled mass production, paving the way for aluminum's widespread adoption across industries. Today, aluminum ranks as the second most produced metal globally, trailing only behind steel.
Key Milestones in Aluminum/Aluminium Development
- 1825: Hans Christian Oersted achieves the first isolation of aluminum.
- 1886: The Hall-Héroult process revolutionizes aluminum production.
- 1950s: Aluminum becomes a cornerstone in aerospace and automotive sectors.
- 2000s: A heightened focus on sustainability and recycling emerges in aluminum production.
Key Properties of Aluminum/Aluminium
Aluminum/aluminium is celebrated for its exceptional combination of properties that render it suitable for a myriad of applications. Its lightweight structure, paired with impressive strength, positions it as an ideal material for industries demanding high-performance materials.
Among the standout properties of aluminum/aluminium are:
- Low Density: Aluminum weighs approximately one-third as much as steel, making it perfect for applications where weight reduction is critical.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum forms a protective oxide layer upon exposure to air, preventing further corrosion.
- Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum's excellent ability to conduct heat and electricity makes it a favored choice for electrical wiring and heat exchangers.
Comparison with Other Metals
When compared to other metals like steel and copper, aluminum offers a distinctive balance of properties. Although steel boasts superior strength, aluminum's lightweight advantage makes it more suitable for scenarios where weight is a concern. Similarly, while copper excels as an electrical conductor, aluminum's lower cost and lighter weight render it a more practical option for many applications.
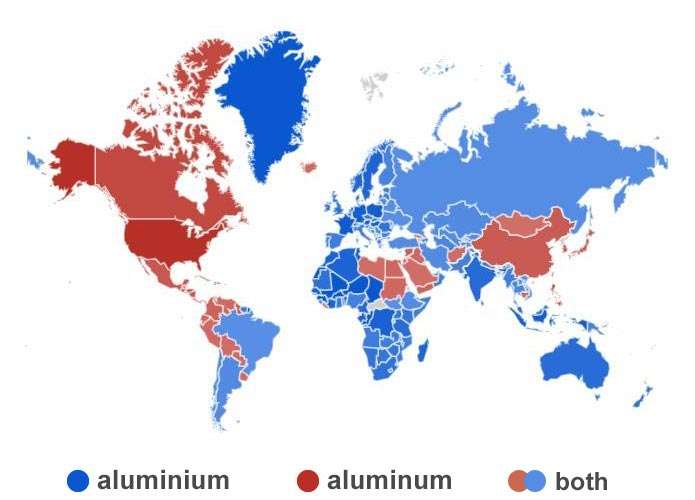
Exploring the Spelling Variations
A frequently asked question about this metal concerns the reason for its differing spellings around the world. The answer resides within the history of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and its naming protocols.
Originally, "aluminium" was proposed by Sir Humphry Davy, the discoverer of the metal. However, American chemists later adopted the spelling "aluminum" to align with other metals such as sodium and potassium. In 1990, IUPAC officially recognized "aluminum" as the standard spelling, although "aluminium" remains prevalent in countries like the UK, Australia, and Canada.
Global Usage of the Terms
- United States: Aluminum
- United Kingdom: Aluminium
- Australia: Aluminium
- Canada: Aluminium
Versatile Applications of Aluminum/Aluminium
Owing to its adaptability and unique properties, aluminum/aluminium finds utility in a broad spectrum of industries. From construction to aerospace, this metal plays a vital role in modern engineering and manufacturing.
Construction Industry
Within the construction sector, aluminum is extensively utilized for window frames, doors, and facades. Its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion make it an excellent choice for buildings situated in coastal areas or regions experiencing harsh weather conditions.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry heavily relies on aluminum due to its impressive strength-to-weight ratio. This characteristic makes aluminum ideal for aircraft components, contributing to reduced fuel consumption and enhanced efficiency.
Automotive Industry
Increasingly, the automotive sector is turning to aluminum for the production of car parts. The metal's lightweight nature aids in improving fuel efficiency and minimizing emissions, making it a favored choice for contemporary vehicles.
Environmental Considerations
While aluminum is a sustainable material, its production process can significantly impact the environment. The extraction and refining of bauxite ore, aluminum's primary source, necessitate substantial energy and can lead to deforestation and habitat destruction.
Nevertheless, aluminum is 100% recyclable, and recycling it consumes merely 5% of the energy required for primary production. This characteristic positions aluminum as one of the most environmentally friendly metals available today.
Recycling Aluminum
- Aluminum can be recycled perpetually without compromising its quality.
- Recycling aluminum conserves up to 95% of the energy required for primary production.
- Global aluminum recycling rates hover around 70%, with considerable potential for enhancement.
The Manufacturing Process
Aluminum production involves multiple stages, commencing with bauxite extraction and culminating in final product fabrication. The process begins with bauxite mining, followed by refining bauxite into alumina using the Bayer process. Subsequently, alumina is converted into aluminum through the Hall-Héroult process, which employs electrolysis.
Key Steps in Aluminum Production
- Bauxite Mining: Bauxite is sourced from mines in countries like Australia, Guinea, and Brazil.
- Alumina Refining: The Bayer process refines bauxite into alumina.
- Electrolysis: The Hall-Héroult process transforms alumina into aluminum via electrolysis.
Industries Benefiting from Aluminum/Aluminium
Aluminum's versatility makes it a critical material in several sectors. Some of the principal industries where aluminum is extensively utilized include:
- Construction: Window frames, doors, and facades.
- Aerospace: Aircraft components and structural parts.
- Automotive: Car parts and body panels.
- Packaging: Beverage cans and food packaging.
Market Growth and Trends
The global aluminum market is anticipated to expand significantly in the forthcoming years, driven by escalating demand in emerging economies. Innovations in aluminum alloys and recycling technologies are expected to further enhance its appeal across industries.
Advantages of Aluminum/Aluminium
Aluminum offers numerous advantages that establish it as a preferred material in various sectors:
- Lightweight: Aluminum's low density reduces weight in applications like automotive and aerospace.
- Corrosion Resistance: Its natural oxide layer provides exceptional protection against corrosion.
- Recyclability: Aluminum is 100% recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Comparative Analysis
In contrast to other metals, aluminum presents a unique blend of properties that render it suitable for a wide array of applications. Its lightweight structure, combined with impressive strength and corrosion resistance, distinguishes it from competitors like steel and copper.
Challenges in Aluminum/Aluminium Production
Despite its many benefits, aluminum production confronts several challenges. The energy-intensive nature of the refining and smelting processes raises concerns about its environmental impact. Additionally, fluctuating prices of bauxite and energy can influence the cost of aluminum production.
Addressing Environmental Concerns
Efforts are underway to diminish the environmental footprint of aluminum production. Innovations in renewable energy sources and enhanced recycling technologies are aiding in mitigating the impact of aluminum production on the environment.
The Future of Aluminum/Aluminium
The future of aluminum appears promising, with rising demand across industries and an increasing emphasis on sustainability. Advances in aluminum alloys and recycling technologies are expected to boost its appeal, making it an even more attractive material for manufacturers.
As the world transitions toward a more sustainable future, aluminum's recyclability and environmental benefits will play a critical role in shaping industries. Its adaptability and versatility make it a material of choice for engineers and manufacturers globally.
Emerging Trends
- Development of advanced aluminum alloys tailored for aerospace and automotive applications.
- Heightened emphasis on sustainable production practices and recycling technologies.
- Increased adoption of aluminum in renewable energy systems and infrastructure projects.
Kesimpulan
In summary, aluminum or aluminium is a material that has profoundly transformed industries worldwide. Its distinctive properties, including lightweight structure, corrosion resistance, and superior conductivity, make it an ideal choice for a broad range of applications. While the spelling difference might seem minor, it reflects the global significance of this material and its extensive usage in diverse regions.
As we advance toward a more sustainable future, aluminum's recyclability and environmental advantages will play a crucial role in shaping industries. Its adaptability and versatility make it a material of choice for engineers and manufacturers globally.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with aluminum in the comments section below. Feel free to explore our additional articles for further insights into materials science and engineering. Together, let’s contribute to a sustainable future!


Detail Author:
- Name : Arielle Ward
- Username : flatley.fay
- Email : patricia40@weimann.com
- Birthdate : 2001-08-26
- Address : 97148 Paxton Passage Suite 691 Goyettemouth, OH 68207
- Phone : 603.457.2323
- Company : Kuhn and Sons
- Job : Aircraft Launch Specialist
- Bio : Facilis consectetur corrupti odit corrupti nobis. Minima omnis provident deserunt provident sint eum quidem incidunt. Eligendi aut deleniti debitis iure. Veniam velit delectus ut vitae ut.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/skunze
- username : skunze
- bio : Aut rerum voluptatem distinctio eligendi qui.
- followers : 2679
- following : 1068
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/kunze1986
- username : kunze1986
- bio : Sed quidem unde sunt dolore. Mollitia ad repellat hic. Excepturi temporibus voluptatum et placeat.
- followers : 2868
- following : 832
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/sofia_kunze
- username : sofia_kunze
- bio : Ab eaque quidem iure. Velit molestias sint ab voluptatem sed.
- followers : 823
- following : 1443
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/skunze
- username : skunze
- bio : Qui quasi asperiores laborum iusto beatae occaecati. Minus nemo ipsum id rerum. Corrupti cupiditate cum et doloremque.
- followers : 1768
- following : 2230