In the modern digital landscape, ensuring robust security has become paramount for organizations operating in the cloud. A Private Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) serves as a cornerstone for securing and isolating cloud environments, empowering businesses to safeguard sensitive data and applications from unauthorized access. By implementing private VPC, companies can maintain efficient connectivity while ensuring compliance with industry standards. This article delves deeply into the concept of private VPC, exploring its advantages, architecture, and practical implementation strategies to assist you in making well-informed decisions for your cloud infrastructure.
As cloud computing continues to expand and evolve, the demand for secure and scalable network solutions has surged. Private VPC stands out as a highly effective solution, enabling enterprises to tailor their cloud environments according to their unique requirements. By creating isolated virtual networks, private VPC ensures that only authorized users and resources gain access to sensitive information, thereby significantly mitigating the risk of cyber threats. This guide aims to provide an all-encompassing understanding of private VPC, catering to both beginners and seasoned IT professionals.
This detailed guide will cover everything you need to know about private VPC, ranging from foundational concepts to advanced configurations. Whether you are just starting your journey into cloud networking or are an experienced professional seeking advanced strategies, this article offers valuable insights for everyone. Let’s explore how private VPC can revolutionize your cloud networking experience and enhance your organization's security posture.
Table of Contents
- What is Private VPC?
- Key Components of Private VPC
- Benefits of Implementing Private VPC
- Private VPC Architecture
- Security Features of Private VPC
- Steps to Implement Private VPC
- Use Cases for Private VPC
- Best Practices for Managing Private VPC
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Future Trends in Private VPC Technology
Understanding the Concept of Private VPC
A private VPC represents a logically isolated virtual network established within a cloud provider's infrastructure. It empowers organizations to define their own IP address range, create subnets, and configure route tables and network gateways. Essentially, private VPC functions as a secure container for cloud resources, ensuring that only authorized entities can interact with them. This isolation is critical for safeguarding sensitive data and applications from potential threats.
One of the most significant advantages of private VPC is its ability to provide a controlled environment where administrators can effectively manage access permissions and monitor network traffic. By leveraging private VPC, businesses can achieve superior control over their cloud resources while ensuring adherence to industry regulations. This capability makes private VPC an indispensable tool for modern cloud-based operations.
Variations of Private VPC Across Cloud Providers
Private VPC offerings differ slightly depending on the cloud provider, each providing unique features tailored to specific use cases. For example:
- Johnny Depp Vanessa Paradis
- Welsh Park Rockville Md
- How Old Mayweather
- Timeless Tours
- Road Closures In Kansas
- AWS VPC: Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a comprehensive VPC solution that supports advanced features such as NAT gateways and VPC peering, enabling seamless communication between multiple VPCs.
- Google Cloud VPC: Google Cloud provides a flexible VPC architecture with support for shared VPCs and global routing, allowing businesses to create scalable and interconnected networks.
- Azure Virtual Network: Microsoft Azure delivers a robust virtual network solution that integrates effortlessly with other Azure services, facilitating efficient resource management and automation.
Key Components of Private VPC
A private VPC comprises several essential components that collaborate to create a secure and efficient virtual network. These components are vital for ensuring the proper functioning and security of the VPC. They include:
- Subnets: Subnets divide the VPC into smaller segments, each with its own IP address range. This segmentation enhances network organization and control, enabling administrators to manage traffic more effectively.
- Route Tables: Route tables determine how traffic flows within and outside the VPC. Administrators can define custom routes to optimize performance and enforce strict security policies, ensuring that only authorized traffic is allowed.
- Internet Gateways: Internet gateways facilitate communication between the VPC and the public internet. They act as a bridge, enabling resources within the VPC to access external networks while maintaining isolation from unauthorized access.
- NAT Gateways: NAT gateways allow instances within private subnets to access the internet without exposing their IP addresses, ensuring that sensitive resources remain protected from external threats.
Advantages of Implementing Private VPC
Implementing a private VPC offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance the security, performance, and scalability of cloud-based operations. Some of the key advantages include:
- Enhanced Security: Private VPC isolates cloud resources from the public internet, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and cyberattacks. This isolation ensures that sensitive data remains protected from external threats.
- Improved Performance: By optimizing network configurations, private VPC ensures faster and more reliable communication between resources, enhancing overall system performance.
- Scalability: Private VPC supports dynamic scaling, enabling businesses to effortlessly add or remove resources as needed to accommodate changing workloads and demands.
- Compliance: Private VPC helps organizations meet industry standards and regulations by providing a secure and controlled environment for sensitive data, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Private VPC Architecture: Designing a Secure and Efficient Network
The architecture of a private VPC is meticulously designed to provide maximum flexibility and security. It typically includes:
- Public Subnets: Public subnets enable resources to communicate directly with the internet through an internet gateway, facilitating external access while maintaining control over network traffic.
- Private Subnets: Private subnets restrict access to resources, ensuring that only authorized entities can interact with them. This isolation is critical for protecting sensitive data and applications.
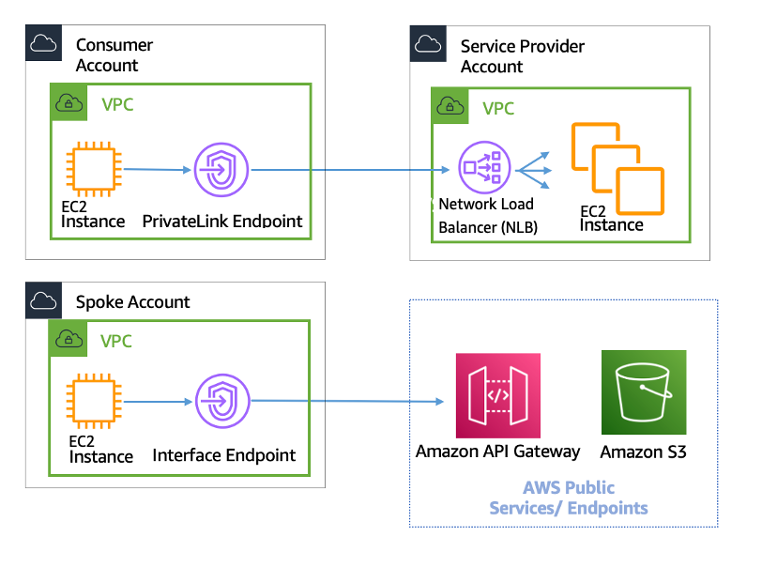
- Peering Connections: VPC peering enables secure communication between multiple VPCs without exposing them to the public internet, facilitating seamless collaboration between different cloud environments.
Design Considerations for Private VPC Architecture
When designing a private VPC architecture, it is essential to consider several critical factors to ensure optimal performance and security. These include:
- Security Policies: Establish clear security policies to govern access to resources within the VPC, ensuring that only authorized personnel can make changes to the configuration.
- Network Segmentation: Segment the VPC into smaller subnets to enhance security and improve performance. Proper segmentation ensures that traffic is managed efficiently and securely.
- Redundancy: Implement redundant components to ensure high availability and fault tolerance, minimizing downtime and enhancing system reliability.
Advanced Security Features of Private VPC
Private VPC incorporates several advanced security features to protect cloud resources from unauthorized access and cyber threats. These features include:
- Firewall Rules: Firewall rules restrict incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined criteria, ensuring that only authorized traffic is allowed to pass through the network.
- Encryption: Data transmitted within the VPC can be encrypted to prevent unauthorized interception and access, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): ACLs provide an additional layer of security by controlling traffic at the subnet level, enabling administrators to enforce strict access policies and monitor network activity.
Steps to Implement Private VPC
Implementing a private VPC involves several key steps to ensure a secure and efficient virtual network. These steps include:
- Define Requirements: Identify the specific needs of your organization and determine the appropriate VPC configuration to meet those requirements.
- Create VPC: Use the cloud provider's console or API to create a new VPC with the desired IP address range, ensuring that it aligns with your organization's network architecture.
- Configure Subnets: Divide the VPC into public and private subnets to ensure proper network segmentation and enhance security by isolating sensitive resources.
- Set Up Gateways: Configure internet and NAT gateways to enable communication between resources and the public internet, ensuring that external access is managed securely and efficiently.
Best Practices for Private VPC Implementation
When implementing private VPC, it is crucial to adhere to best practices to ensure optimal performance and security. These practices include:
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure that security policies are being followed and that configurations remain up-to-date, minimizing the risk of vulnerabilities and breaches.
- Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to track network activity and detect potential security threats in real-time, enabling prompt action to address any issues that arise.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of VPC configurations and changes to facilitate troubleshooting and future updates, ensuring that all stakeholders have access to accurate information.
Practical Use Cases for Private VPC
Private VPC is versatile and suitable for a wide range of use cases, addressing diverse organizational needs. Some common use cases include:
- Web Hosting: Host websites and applications securely within a private VPC to protect sensitive customer data and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
- Database Management: Store and manage databases within a private VPC to ensure data integrity, confidentiality, and high availability, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Hybrid Cloud Solutions: Connect on-premises infrastructure with cloud resources using private VPC to create a seamless hybrid environment that supports both legacy systems and modern cloud applications.
Best Practices for Managing Private VPC
Effectively managing a private VPC requires adherence to best practices to ensure optimal performance, security, and reliability. These practices include:
- Regular Updates: Keep all components of the VPC up-to-date with the latest security patches and software updates to address vulnerabilities and enhance system resilience.
- Access Control: Implement strict access control policies to ensure that only authorized personnel can make changes to the VPC configuration, minimizing the risk of unauthorized modifications.
- Disaster Recovery: Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan to minimize downtime in the event of a failure or security breach, ensuring business continuity and data protection.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Private VPC
When working with private VPC, several common issues may arise that can impact performance and security. These include:
- Connectivity Problems: Verify route tables and security groups to ensure proper configuration and resolve any connectivity issues that may arise.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Monitor network traffic and optimize resource allocation to improve performance and ensure that the VPC operates efficiently under varying workloads.
- Security Breaches: Investigate any suspicious activity and update security policies as needed to prevent future breaches and enhance the overall security posture of the VPC.
Future Trends in Private VPC Technology
The future of private VPC technology is promising, with several exciting trends on the horizon that will further enhance its capabilities. These trends include:
- Automated Configurations: Advances in automation will simplify the process of setting up and managing private VPCs, reducing the need for manual intervention and enabling organizations to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Security: Emerging technologies such as AI and machine learning will improve the ability to detect and respond to security threats in real-time, enhancing the overall security of cloud environments.
- Global Networking: Cloud providers will continue to expand their global infrastructure, enabling businesses to create private VPCs with seamless connectivity across regions, facilitating global operations and collaboration.
Conclusion
Private VPC is an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to enhance their cloud networking capabilities. By providing a secure, isolated environment for cloud resources, private VPC helps protect sensitive data and

Detail Author:
- Name : Santino Rohan
- Username : torrey.cruickshank
- Email : haley.ankunding@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1978-06-22
- Address : 479 Otilia Coves Apt. 612 Nikolausfort, TX 52394
- Phone : +19299294528
- Company : Champlin, Schoen and Frami
- Job : Streetcar Operator
- Bio : Commodi est quisquam sed voluptas. Ea eum sed ut ut quia nobis delectus autem. Cum nisi alias libero voluptas nulla nisi.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/kevon5545
- username : kevon5545
- bio : Non id dolor dolore itaque molestias. Debitis repellat porro accusamus et. Minus quia quisquam similique. Sed nihil perferendis dicta.
- followers : 3983
- following : 2332
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/kevon5954
- username : kevon5954
- bio : Unde qui hic fugit non unde eos voluptas.
- followers : 1023
- following : 726
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/schmidt2012
- username : schmidt2012
- bio : Consequatur pariatur est aut est.
- followers : 6152
- following : 129