Wi-Fi has become an indispensable part of our daily routines, enabling seamless connectivity across countless devices and fundamentally altering the way we communicate, work, and entertain ourselves. It’s hard to imagine a world without Wi-Fi—streaming movies, browsing social media, or working remotely would be nearly impossible. The development of Wi-Fi technology is a remarkable story of innovation, collaboration, and technological advancement that has revolutionized modern communication. Exploring the history of Wi-Fi provides invaluable insights into how this groundbreaking technology has evolved over the years.
From its modest beginnings as a basic wireless communication protocol to its current role as the backbone of modern internet connectivity, Wi-Fi has undergone significant transformations. This article delves deeply into the history of Wi-Fi, examining its origins, pivotal milestones, and the individuals who played a key role in its development. By understanding the timeline of Wi-Fi, we can appreciate the dedication and efforts of engineers, researchers, and organizations that have contributed to its evolution.
In this thorough guide, we will explore the fascinating journey of Wi-Fi technology, analyzing its roots, key advancements, and future potential. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a student, or simply curious about the mechanics of Wi-Fi, this article will provide you with a wealth of knowledge about the history of wireless connectivity.
Table of Contents
- The Origins of Wi-Fi
- Key Developments in Wi-Fi Technology
- Evolution of Wi-Fi Standards
- Major Milestones in Wi-Fi Timeline
- The Role of Wi-Fi Organizations
- Benefits of Wi-Fi Technology
- Challenges in Wi-Fi Development
- Future Trends in Wi-Fi Technology
- Real-World Applications of Wi-Fi
- Conclusion
The Beginnings of Wi-Fi
The story of Wi-Fi begins with the development of wireless communication technologies in the early 20th century. The concept of wireless transmission can be traced back to the groundbreaking experiments of Nikola Tesla and Guglielmo Marconi, who laid the foundation for radio communication. However, it wasn't until the late 20th century that wireless networking technology started to take shape.
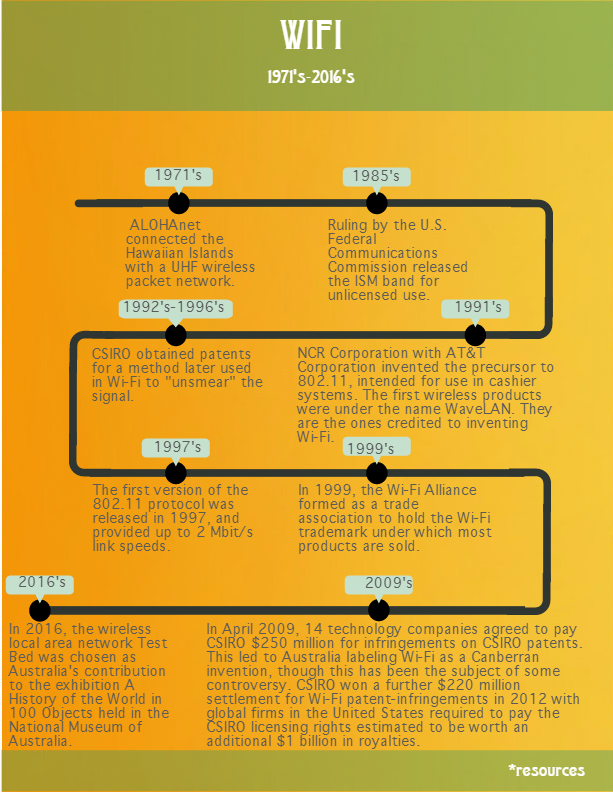
In the 1970s, the University of Hawaii developed ALOHAnet, one of the earliest wireless computer networks. This pioneering system used radio waves to connect computers across the Hawaiian islands, establishing a foundation for modern wireless communication. Although ALOHAnet was not the Wi-Fi we know today, it demonstrated the immense potential of wireless networking in connecting remote devices.
By the 1980s, advancements in radio frequency technology and the establishment of the IEEE 802.11 standard marked the beginning of Wi-Fi's journey. The IEEE 802.11 standard provided a framework for wireless communication, enabling devices to connect without the need for physical cables. This standardization was vital in ensuring compatibility and driving the widespread adoption of Wi-Fi technology.
- S In Walnut Creek
- Temperature For Medium Rareteak
- Dodgercore Today
- Joe Biden Political Career
- Moody Blues Question Lyrics
Pivotal Advances in Wi-Fi Technology
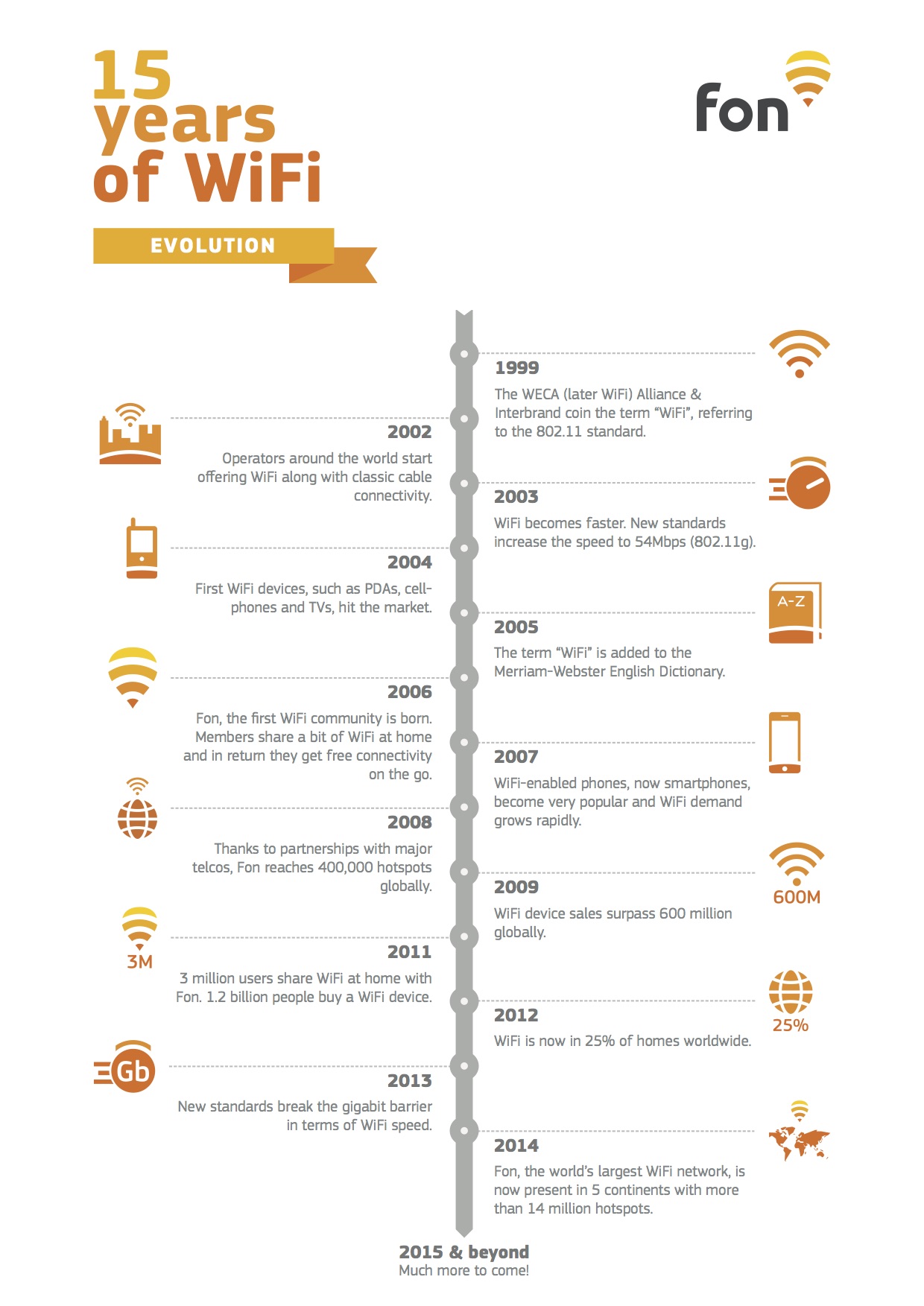
Wi-Fi technology has experienced significant advancements since its inception. A major turning point was the introduction of the IEEE 802.11b standard in 1999, which offered faster data transfer rates and improved reliability. This standard, commonly referred to as Wi-Fi, became the cornerstone of modern wireless networking.
Subsequent iterations of the IEEE 802.11 standard, such as 802.11g, 802.11n, and 802.11ac, have continued to enhance Wi-Fi performance. Each new standard has introduced improvements in speed, range, and efficiency, addressing the ever-growing demands of internet users. The latest standard, Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), promises even faster speeds and superior performance in crowded environments.
These advancements have been driven by breakthroughs in semiconductor technology, antenna design, and network protocols. Researchers and engineers have worked tirelessly to overcome technical challenges, ensuring that Wi-Fi remains at the forefront of wireless communication.
The Progression of Wi-Fi Standards
The evolution of Wi-Fi standards has been instrumental in the advancement of wireless technology. Each new standard has introduced enhancements in speed, range, and efficiency, meeting the increasing demands of internet users.
IEEE 802.11b
Released in 1999, the IEEE 802.11b standard was the first widely adopted Wi-Fi standard. It offered data transfer rates of up to 11 Mbps and became the foundation for modern wireless networking. Although slower by today's standards, it represented a significant leap forward compared to earlier wireless technologies.
IEEE 802.11g
Introduced in 2003, the IEEE 802.11g standard offered data transfer rates of up to 54 Mbps, making it significantly faster than its predecessor. It also introduced improvements in reliability and range, making it suitable for a broader range of applications.
IEEE 802.11n
The IEEE 802.11n standard, released in 2009, marked a major breakthrough in Wi-Fi technology. It incorporated multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology, enabling data transfer rates of up to 600 Mbps. This standard also improved range and reliability, making it ideal for high-bandwidth applications.
Defining Moments in the Wi-Fi Timeline
The history of Wi-Fi is marked by several key milestones that have shaped its development. These milestones represent significant achievements in wireless communication technology and underscore the collaborative efforts of engineers, researchers, and organizations.
- 1971: ALOHAnet, the first wireless computer network, is developed by the University of Hawaii.
- 1985: The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) designates the 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, and 5 GHz bands for unlicensed use, paving the way for Wi-Fi development.
- 1997: The IEEE 802.11 standard is introduced, providing a framework for wireless communication.
- 1999: The IEEE 802.11b standard is released, marking the beginning of widespread Wi-Fi adoption.
- 2003: The IEEE 802.11g standard is introduced, offering faster data transfer rates and improved reliability.
The Influence of Wi-Fi Organizations
Several organizations have played a critical role in the development and promotion of Wi-Fi technology. The Wi-Fi Alliance, founded in 1999, is a global organization that certifies Wi-Fi products and ensures interoperability between devices. Through its certification programs, the Wi-Fi Alliance has helped establish Wi-Fi as a reliable and widely adopted technology.
Other organizations, such as the IEEE and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), have contributed to the development of Wi-Fi standards and regulations. These organizations collaborate closely with governments, industry stakeholders, and researchers to ensure that Wi-Fi technology meets the needs of users around the world.
The Advantages of Wi-Fi Technology
Wi-Fi technology offers numerous benefits that have transformed the way we live and work. Below are some of the key advantages of Wi-Fi:
Convenience and Accessibility
Wi-Fi provides unparalleled convenience by enabling users to access the internet from virtually anywhere. Whether at home, in the office, or in public spaces, Wi-Fi ensures seamless connectivity without the need for physical cables. This accessibility has made it an essential part of our daily lives.
Cost Efficiency
Compared to wired networks, Wi-Fi offers significant cost advantages by eliminating the need for expensive cabling and infrastructure. This makes it an attractive option for businesses and individuals looking to reduce costs while maintaining high-quality connectivity.
Flexibility in Connectivity
Wi-Fi allows users to connect a wide variety of devices, from smartphones and laptops to smart home appliances and IoT devices. This flexibility has made Wi-Fi an indispensable component of modern digital ecosystems.
The Challenges Facing Wi-Fi Development
Despite its many benefits, Wi-Fi technology faces several challenges that must be addressed to ensure its continued success. These challenges include:
- Interference: Wi-Fi operates in unlicensed frequency bands, making it vulnerable to interference from other devices and networks.
- Security: Ensuring secure communication over Wi-Fi networks remains a critical concern, particularly in public spaces where data privacy is paramount.
- Capacity: As the number of connected devices continues to grow, Wi-Fi networks must be able to handle increasing levels of traffic without compromising performance.
Emerging Trends in Wi-Fi Technology
The future of Wi-Fi is bright, with several emerging trends set to shape its development. These trends include:
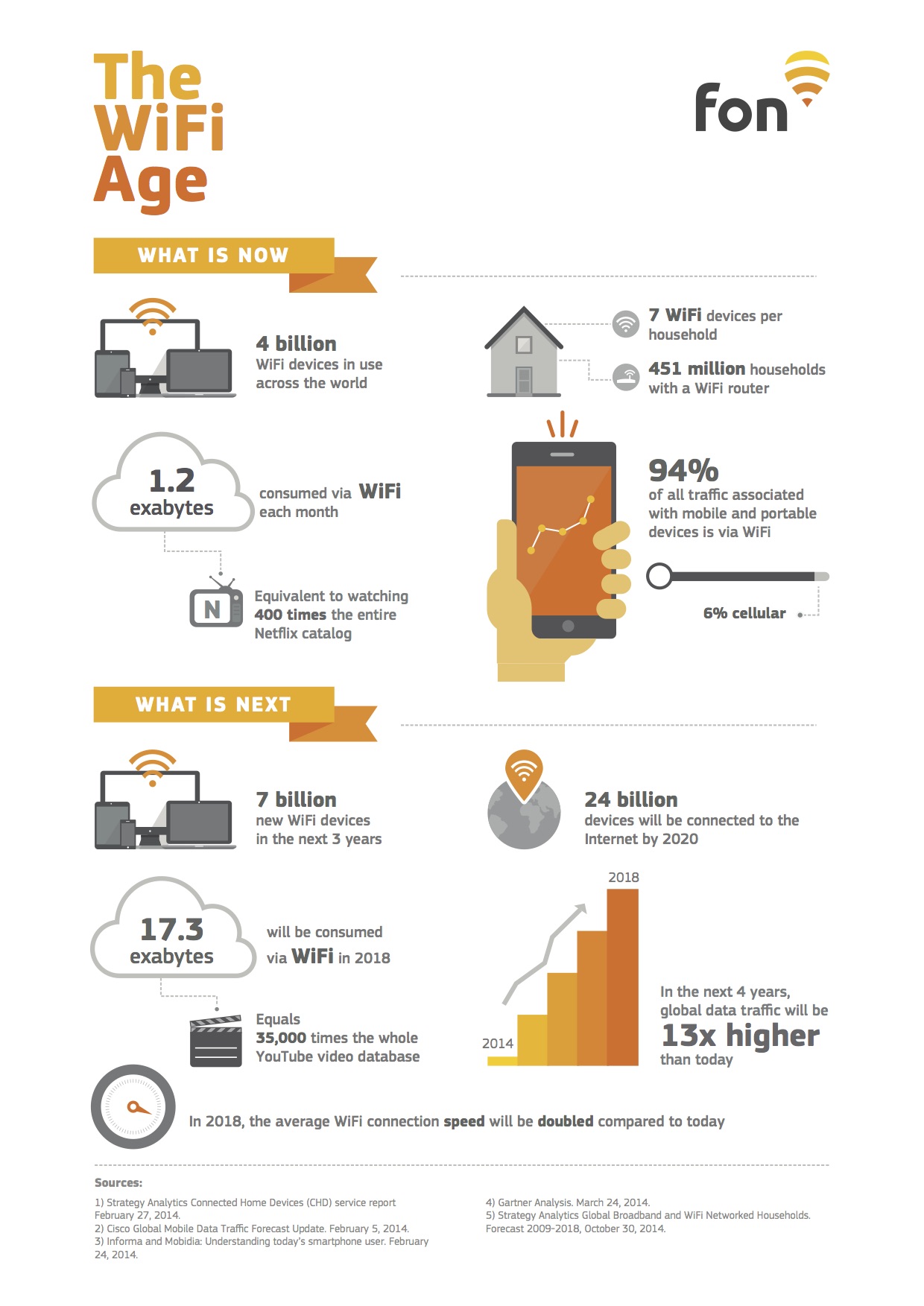
- Wi-Fi 6 and Beyond: The latest Wi-Fi 6 standard promises faster speeds, better performance, and improved efficiency. Future versions, such as Wi-Fi 7, will build on these advancements, paving the way for even more innovative possibilities.
- 5G Integration: The integration of Wi-Fi with 5G networks will enhance connectivity and provide seamless transitions between wireless technologies, offering users an uninterrupted experience.
- IoT Expansion: As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, Wi-Fi will play a crucial role in connecting smart devices and enabling smart homes, cities, and industries.
Practical Applications of Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi technology has found applications in various fields, transforming industries and improving quality of life. Some of the key applications include:
- Smart Homes: Wi-Fi enables the connection of smart devices, allowing users to control lighting, temperature, and security systems remotely, enhancing convenience and energy efficiency.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, Wi-Fi facilitates telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, and the operation of advanced medical devices, improving patient care and outcomes.
- Education: Wi-Fi has revolutionized education by enabling online learning, virtual classrooms, and access to a wealth of digital resources, making education more accessible and engaging.
Final Thoughts
The history of Wi-Fi is a testament to the power of innovation and collaboration in shaping modern technology. From its humble beginnings as a basic wireless communication protocol to its current role as the backbone of internet connectivity, Wi-Fi has come a long way. Understanding its evolution provides invaluable insights into its potential to transform the future of communication.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Wi-Fi technology in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others. For more insights into technology and innovation, explore our other articles on our website.
Detail Author:
- Name : Sheila O'Conner
- Username : fkozey
- Email : jhyatt@senger.com
- Birthdate : 2006-10-21
- Address : 170 Wilber Courts New Thaddeus, IL 00737
- Phone : 640-581-5921
- Company : Wyman and Sons
- Job : Order Filler OR Stock Clerk
- Bio : Necessitatibus sed reprehenderit dolor tempora enim dolorem enim. Veniam aut voluptas qui error accusamus qui ullam. Ab quas rem ad perspiciatis beatae aut vel.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/cschumm
- username : cschumm
- bio : Est dolor et ex et vel. Commodi voluptatibus labore autem fuga accusamus.
- followers : 3272
- following : 1752
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@chris.schumm
- username : chris.schumm
- bio : Corporis adipisci voluptatem et dolorem vero tenetur est.
- followers : 1932
- following : 847
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/chris1783
- username : chris1783
- bio : Voluptas sed at et. Error ipsam atque ad qui. Quam a et quisquam consequatur.
- followers : 6827
- following : 1941
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/chris6000
- username : chris6000
- bio : Optio excepturi atque nemo dolorem et adipisci accusantium. Non sed repellendus explicabo rerum ipsum.
- followers : 4852
- following : 241
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/chris_xx
- username : chris_xx
- bio : Voluptatem vel ut et.
- followers : 6680
- following : 2991