Calories and kcal are terms commonly encountered in the realm of nutrition, yet their distinctions often remain unclear to many. Both units quantify energy, but understanding their nuances is essential for maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle. This article aims to clarify these terms and provide actionable insights into how they impact our daily dietary decisions.
The ongoing discussion about calories versus kcal has gained momentum with the rise of fitness enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals. Many people question whether they are consuming the appropriate amount of energy to meet their body’s requirements. This article will delve into the intricacies of these terms, highlighting their significance in nutrition.
Whether your goal is weight loss, muscle gain, or maintaining your current fitness level, grasping the concepts of calories and kcal is indispensable. By the conclusion of this article, you will possess a thorough understanding of these principles and how they influence your overall health and well-being.
- Connecticut Department Of Motor Vehicles Norwalk
- Center For Reproductive Rights
- Jaguars Qbs
- How Old Jack Black
- Welsh Park Rockville Md
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Are Calories?
- What Are kcal?
- Calories vs kcal: Unpacking the Differences
- Energy Measurement in Daily Life
- Calories in Food
- Daily Caloric Needs
- Calories and Weight Management
- Calories and Exercise
- Myths About Calories
- Conclusion
What Are Calories?
Calories serve as units of energy that quantify the heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius. Within the context of nutrition, calories reflect the energy content present in food and beverages. Grasping this foundational concept is pivotal for anyone aiming to regulate their diet efficiently.
History of the Calorie
The term "calorie" was introduced in the 19th century by Nicolas Clément, a French physicist. Initially utilized in chemistry to measure heat energy, the concept was later adapted to nutrition, becoming a standard for evaluating energy intake. Understanding the historical context of calories provides deeper insight into their role in modern dietary practices.
Here are some essential aspects of calories:
- Calories are indispensable for vital bodily functions, including metabolism, movement, and growth.
- Excessive or insufficient calorie consumption can lead to significant health challenges, such as obesity or malnutrition.
- Calories are derived from macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, each contributing differently to overall energy levels.
What Are kcal?
kcal, or kilocalories, measures the energy necessary to raise the temperature of one kilogram of water by one degree Celsius. In everyday terminology, kcal is frequently used synonymously with "calories" when discussing food energy. However, kcal denotes a significantly larger unit of energy compared to a single calorie.
Why kcal Matters in Nutrition
kcal is the globally recognized unit in nutritional labeling, helping consumers make informed dietary decisions. Food packaging typically displays energy content in kcal, emphasizing its importance for balancing energy intake with expenditure. Understanding kcal is crucial for anyone striving to manage their diet effectively.
Here are some essential facts about kcal:
- One kcal is equivalent to 1,000 calories.
- kcal is widely used in scientific research related to nutrition and metabolism, providing a standardized measure for energy.
- kcal offers a more precise measurement of energy for human consumption compared to individual calories.
Calories vs kcal: Unpacking the Differences
The fundamental distinction between calories and kcal lies in their scale of measurement. While calories represent smaller units of energy, kcal encompasses larger units, making this differentiation critical when interpreting nutritional data.
Understanding the Conversion
Converting between calories and kcal is simple: one kcal equals 1,000 calories. For instance, if a food item contains 200 kcal, it equates to 200,000 calories of energy. This conversion aids in clarifying the energy content of food and beverages, ensuring accurate dietary tracking.
Here’s a concise comparison:
- Calories: A smaller unit of energy, often utilized in scientific contexts.
- kcal: A larger unit of energy, predominantly used in nutrition and daily life.
Energy Measurement in Daily Life
Tracking energy intake and expenditure is fundamental to sustaining a healthy lifestyle. Both calories and kcal play vital roles in this process. By comprehending how much energy we consume and burn, we can make more informed decisions regarding our diet and exercise routines.
Tools for Energy Measurement
Modern advancements have simplified the tracking of energy intake and expenditure. Devices like smartwatches and fitness apps enable individuals to monitor their daily caloric intake and physical activity levels. These tools offer valuable insights into how calories and kcal influence overall health.
Here are some popular tools:
- Smartwatches: Track steps, heart rate, and calories burned, providing real-time feedback.
- Food tracking apps: Calculate daily kcal intake based on food consumption, promoting mindful eating.
- Metabolic tests: Measure resting metabolic rate, helping determine baseline energy needs.
Calories in Food
The calorie content of foods varies significantly depending on their composition. Macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats contribute differently to the total energy content of a meal. Understanding the calorie content of various foods is essential for making informed dietary choices.
Macronutrient Breakdown
Below is a detailed breakdown of how macronutrients contribute to calorie content:
- Carbohydrates: Provide 4 kcal per gram, serving as a primary energy source.
- Proteins: Supply 4 kcal per gram, essential for muscle repair and growth.
- Fats: Deliver 9 kcal per gram, offering a concentrated energy source.
This information underscores the importance of balancing macronutrient intake to meet daily energy requirements while avoiding excessive calorie consumption.
Daily Caloric Needs
Each individual’s daily caloric needs vary based on factors such as age, gender, weight, and activity level. Calculating these requirements is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and supporting overall well-being.
Factors Influencing Caloric Needs
Here are some key factors that shape daily caloric requirements:
- Age: Metabolic rate declines with age, reducing caloric needs.
- Gender: Men typically require more calories than women due to differences in muscle mass and metabolism.
- Activity level: Higher physical activity increases caloric needs.
- Weight goals: Individuals aiming to lose weight may need to reduce calorie intake, while those seeking weight gain may need to increase it.
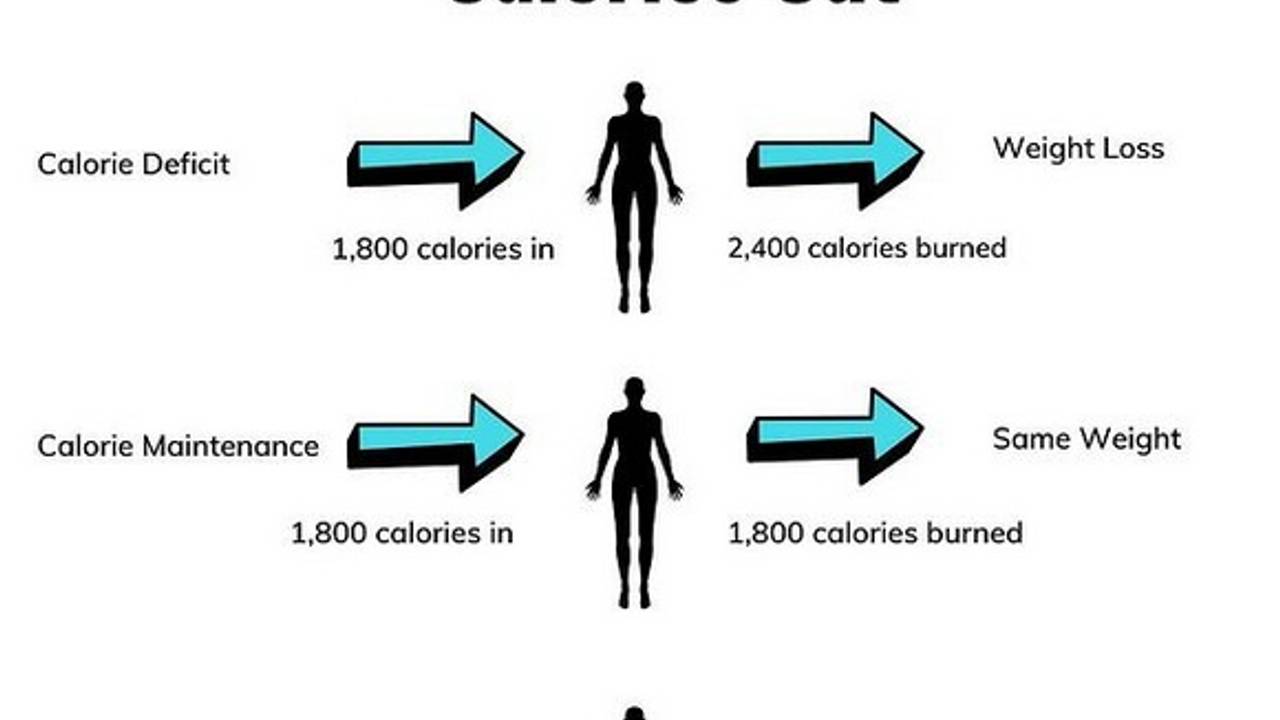
Calories and Weight Management
Calories play a pivotal role in weight management. Consuming more calories than the body burns results in weight gain, while consuming fewer calories leads to weight loss. Achieving a balance between calorie intake and expenditure is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight.
Tips for Managing Calories
Here are some practical strategies for managing calorie intake:
- Track your daily kcal intake using a food diary or app to gain better control over your diet.
- Prioritize nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins and minerals without excessive calories, promoting overall health.
- Incorporate regular physical activity to increase calorie expenditure, enhancing weight management efforts.
Calories and Exercise
Exercise is an effective method for burning calories and improving overall fitness. Different types of physical activity burn varying amounts of kcal, depending on intensity and duration. Understanding how exercise affects calorie expenditure can empower individuals to achieve their health and fitness objectives.
Caloric Expenditure During Exercise
Below is an estimate of kcal burned during common exercises:
- Walking (3 mph): Approximately 150 kcal per hour, ideal for low-impact fitness.
- Running (6 mph): Roughly 600 kcal per hour, providing an intense cardiovascular workout.
- Cycling (12 mph): Around 300 kcal per hour, offering a versatile and enjoyable activity.
These figures serve as a general guideline for estimating energy expenditure during physical activity, aiding in effective workout planning.
Myths About Calories
Several misconceptions surrounding calories and kcal can lead to confusion. Dispelling these myths is essential for making informed dietary decisions.
Common Myths
Here are some prevalent myths about calories:
- All calories are the same: While calories measure energy, the source of calories significantly impacts overall health and nutrient intake.
- Counting calories is unnecessary: Monitoring calorie intake can be highly beneficial for weight management and overall health, providing structure and awareness.
- Low-calorie diets are always healthy: Restrictive diets may lead to nutrient deficiencies and other health issues, emphasizing the importance of balanced nutrition.
Conclusion
Grasping the distinction between calories and kcal is essential for managing your diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Both units measure energy, but kcal offers a more practical and applicable measure for everyday use. By balancing your caloric intake with your energy expenditure, you can effectively achieve your health and fitness aspirations.
We encourage you to apply the knowledge gained from this article to make informed dietary decisions. Share your thoughts in the comments below and explore additional articles on our site for further insights into nutrition and health. Together, let’s work towards a healthier future!
References:
- World Health Organization. (2021). Healthy Diet. Retrieved from https://www.who.int
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2020). Calories Burned in Common Exercises. Retrieved from https://www.health.harvard.edu
- U.S. Department of Agriculture. (2022). Dietary Guidelines for Americans. Retrieved from https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov


Detail Author:
- Name : Mrs. Jewel Treutel PhD
- Username : blick.jimmy
- Email : abayer@cummings.com
- Birthdate : 1993-06-09
- Address : 35027 Deshawn Motorway Port Napoleon, MN 33973-6287
- Phone : 1-832-287-7615
- Company : Ortiz-Hansen
- Job : Directory Assistance Operator
- Bio : Corporis sunt fugiat ipsum officiis. Qui iusto voluptatem voluptatem voluptatem quos unde. Autem rerum corporis ut architecto.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/mitchell_xx
- username : mitchell_xx
- bio : Beatae quidem aut minus aperiam quasi ipsa. Ipsa et id quia qui neque.
- followers : 3250
- following : 1922
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/mitchell1224
- username : mitchell1224
- bio : Dolorum inventore laborum pariatur rerum.
- followers : 3657
- following : 2431
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/wildermanm
- username : wildermanm
- bio : Incidunt quia vel minima optio minus. Nesciunt molestias sunt ea qui deleniti. Eum eos et animi omnis molestiae. Aut dicta dolorem aut.
- followers : 4847
- following : 2587