Testing positive for HSV-2 IGG signifies a past exposure to the Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2, a condition that affects millions worldwide. HSV-2 is a prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI) that, while manageable, requires awareness and proactive health management. Learning about its implications, symptoms, transmission, and treatment options can significantly enhance one’s ability to cope with the condition effectively.
This article delves into the complexities of HSV-2 IGG positive, exploring its potential risks, symptoms, transmission pathways, treatment strategies, and preventive measures. By referencing scientific studies and expert advice, we aim to empower readers with actionable knowledge to make informed decisions about their sexual health. Whether you're newly diagnosed or simply seeking more information, this guide is designed to provide clarity and support.
Join us as we break down the basics of HSV-2 and its implications when IgG antibodies are detected. This resource will serve as a comprehensive roadmap to navigating life with HSV-2 while promoting understanding and reducing stigma.
- So Cal Edison Blackouts
- San Juan County Tax Assessor Nm
- Tom And Jerry 2020 Cast
- Temperature For Medium Rareteak
- Alice Braga Moraes
Table of Contents
- Exploring HSV-2: What It Is and Its Global Impact
- Understanding IgG Antibodies: The Role They Play in Diagnosis
- Interpreting HSV-2 IGG Positive: What It Really Means
- Recognizing Symptoms: What to Look For
- How HSV-2 Spreads: Transmission Dynamics
- Diagnosing HSV-2: Methods and Approaches
- Managing HSV-2: Treatment Options and Strategies
- Preventing HSV-2: Practical Steps for Protection
- The Emotional Impact of HSV-2: Coping and Support
- Conclusion: Thriving with HSV-2
Exploring HSV-2: What It Is and Its Global Impact
HSV-2, or Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2, is a viral infection predominantly associated with genital herpes. Unlike HSV-1, which is commonly linked to oral herpes, HSV-2 primarily affects the genital region. According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 491 million individuals aged 15-49 worldwide are infected with HSV-2. This staggering figure underscores the importance of understanding and managing the condition.
HSV-2 vs. HSV-1: Key Differences
- HSV-2 is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, making it a significant concern for sexual health.
- In contrast, HSV-1 is often spread through non-sexual interactions, such as kissing or sharing utensils.
- While both viruses can cause genital herpes, HSV-2 is more prone to recurring outbreaks, making it a persistent challenge for those affected.
Although HSV-2 is a lifelong condition, it can be effectively managed with the right combination of treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Early detection and a comprehensive understanding of the virus are critical for minimizing its impact on daily life and overall well-being.
Understanding IgG Antibodies: The Role They Play in Diagnosis
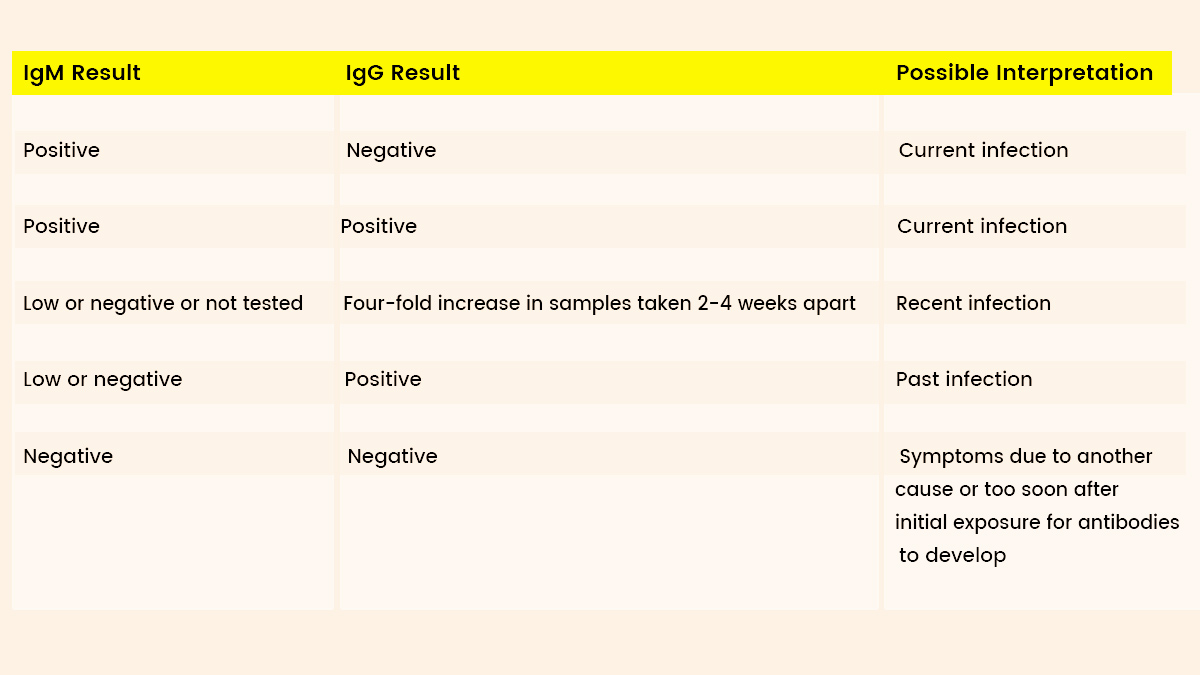
Antibodies are specialized proteins produced by the immune system in response to infections or pathogens. Among these, IgG antibodies are the most prevalent type found in the blood. They play a pivotal role in long-term immunity, offering protection against previously encountered pathogens. When an individual tests positive for HSV-2 IgG, it indicates that their body has been exposed to the virus and has developed antibodies to combat it.
Types of Antibodies in HSV Testing
- IgM: These antibodies signal a recent or acute infection, often indicating the body's initial response to the virus.
- IgG: These antibodies reflect a past infection and the development of long-term immunity. Their presence is crucial for diagnosing HSV-2, especially in cases where symptoms are mild or absent.
It’s important to note that while IgG antibodies confirm past exposure to HSV-2, they do not guarantee immunity against future outbreaks. Understanding the nuances of antibody testing is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management of the condition.
Interpreting HSV-2 IGG Positive: What It Really Means
An HSV-2 IgG positive result signifies that the individual has been exposed to Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 at some point in their life. This outcome confirms a past infection, even if the person has not experienced noticeable symptoms. In fact, many individuals remain asymptomatic, making it difficult to pinpoint when or how they were infected. This asymptomatic nature of HSV-2 underscores the importance of regular testing and awareness.
Implications of HSV-2 IGG Positive
- Increased likelihood of transmitting the virus to others, particularly during active outbreaks or through asymptomatic shedding.
- Potential for recurring outbreaks, though the frequency and severity vary widely among individuals.
- Heightened vulnerability to other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), emphasizing the need for proactive sexual health management.
Understanding the implications of an HSV-2 IgG positive result is fundamental for effective condition management and prevention of transmission. Consulting a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance and support tailored to individual needs.
Recognizing Symptoms: What to Look For
While some individuals with HSV-2 may experience no symptoms, others may encounter noticeable signs during an outbreak. Common symptoms include:
- Painful blisters or sores in the genital area, which can cause discomfort and distress.
- Itching or tingling sensations in the affected region, often preceding the appearance of sores.
- Pain during urination, a symptom that can exacerbate discomfort and affect daily activities.
- Flu-like symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes, which may accompany initial outbreaks.
The frequency and intensity of outbreaks vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience only a few episodes throughout their lifetime, while others may face more frequent recurrences. Recognizing these symptoms early on is crucial for seeking timely medical attention and initiating appropriate treatment.
How HSV-2 Spreads: Transmission Dynamics
HSV-2 is primarily transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Notably, the virus can be spread even in the absence of visible symptoms, a phenomenon known as asymptomatic shedding. This characteristic makes HSV-2 particularly challenging to control and underscores the importance of safe sexual practices.
Factors Influencing Transmission
- The presence of active sores or lesions significantly increases the likelihood of transmission.
- The frequency of outbreaks also plays a role, as higher recurrence rates correlate with greater transmission risks.
- Using protection, such as condoms, during sexual activity can substantially reduce the risk of transmission, though it does not eliminate it entirely.
Educating oneself and partners about safe sexual practices is vital for reducing the spread of HSV-2. Open and honest communication about STI status is another critical component of prevention.
Diagnosing HSV-2: Methods and Approaches
Accurate diagnosis of HSV-2 typically involves a combination of physical examination and laboratory testing. The most widely used method is the HSV-2 IgG blood test, which detects the presence of antibodies specific to the virus. This test is particularly valuable for identifying HSV-2 in individuals who may be asymptomatic or experiencing mild symptoms.
Other Diagnostic Methods
- Viral culture: This involves collecting a sample from an active sore for detailed analysis, providing a definitive diagnosis.
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): This advanced technique detects the genetic material of the virus, offering rapid and precise results.
Early diagnosis is essential for effective management of HSV-2, enabling individuals to take proactive steps in minimizing its impact on their quality of life. Consulting a healthcare professional is the first and most important step in obtaining an accurate diagnosis and developing a suitable treatment plan.
Managing HSV-2: Treatment Options and Strategies
While there is currently no cure for HSV-2, antiviral medications can significantly alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks. Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Acyclovir
- Valacyclovir
- Famciclovir
These medications can be administered episodically during outbreaks or as suppressive therapy to prevent recurrences. In addition to medication, adopting healthy lifestyle practices such as stress management, regular exercise, and a balanced diet can further enhance the body’s ability to manage the condition effectively.
Preventing HSV-2: Practical Steps for Protection
Preventing the transmission of HSV-2 requires a multifaceted approach that combines education, awareness, and safe sexual practices. Key strategies include:
- Consistently and correctly using condoms during sexual activity to minimize transmission risks.
- Avoiding sexual contact during outbreaks or when symptoms are present, as this is when the virus is most contagious.
- Engaging in open and honest discussions with sexual partners about STI status to foster mutual understanding and protection.
While these measures can greatly reduce the likelihood of transmission, they do not eliminate it entirely. Regular STI screenings and staying informed about sexual health are essential components of comprehensive prevention.
The Emotional Impact of HSV-2: Coping and Support
Receiving an HSV-2 diagnosis can evoke a range of emotions, including stigma, shame, and anxiety about the future. It’s important to recognize that HSV-2 is a common and manageable condition. Seeking support is crucial for navigating the emotional challenges associated with the diagnosis.
Strategies for Emotional Well-being
- Connecting with support groups or online communities to share experiences and gain insights from others in similar situations.
- Engaging in therapy or counseling to address emotional concerns and develop coping strategies.
- Staying informed about HSV-2 to dispel myths and reduce fear and uncertainty surrounding the condition.
By fostering a positive mindset and building a supportive network, individuals with HSV-2 can lead fulfilling and healthy lives, free from unnecessary stigma or fear.
Conclusion: Thriving with HSV-2
Testing positive for HSV-2 IGG may initially seem overwhelming, but with the right knowledge, resources, and support, it can be effectively managed. Understanding the virus, its transmission pathways, and available treatment options empowers individuals to take control of their health and well-being. By practicing safe sexual behaviors, seeking regular medical care, and addressing emotional concerns, those living with HSV-2 can lead thriving and fulfilling lives.
We encourage readers to share this article with others who may benefit from the information and to leave comments or questions below. For more in-depth insights into sexual health, explore our other articles on related topics. Together, we can promote awareness, reduce stigma, and support those affected by HSV-2 and other sexually transmitted infections.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-does-a-positive-herpes-igg-test-mean-31329371-5b95b9c6c9e77c0082f5a37e.png)
Detail Author:
- Name : Miss Katherine Hodkiewicz III
- Username : wreinger
- Email : abbey.wunsch@bailey.com
- Birthdate : 1988-10-30
- Address : 98829 Alexa Brooks East Virgilmouth, OK 12210
- Phone : (240) 954-9728
- Company : Gutmann LLC
- Job : Physical Therapist
- Bio : Voluptas quo tempora sit. Qui blanditiis tenetur asperiores deserunt. Tempore dignissimos cupiditate non dolorem dolor.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/moraro
- username : moraro
- bio : Quia ullam quisquam ut excepturi. Quo nihil maxime sed est aut. Amet impedit beatae laboriosam modi.
- followers : 6196
- following : 2321
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/orpha.morar
- username : orpha.morar
- bio : Fugiat consectetur a tempore tenetur molestiae ipsum.
- followers : 2397
- following : 2869
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/orphamorar
- username : orphamorar
- bio : Cupiditate quae repellendus et quod quisquam.
- followers : 2872
- following : 773