Calories are a fundamental concept in nutrition, yet the distinction between "cal" and "calories" often causes confusion. Grasping these terms is crucial for maintaining a balanced diet and achieving health goals. This article aims to clarify the differences and provide practical advice to help you make smarter dietary choices.
Whether you're a fitness enthusiast, a health-conscious individual, or simply someone looking to enhance your nutritional knowledge, this guide will cover everything you need to know about the difference between cal and calories. By the end, you'll have a deeper understanding of how these concepts impact your health and well-being.
As we explore this topic, we'll delve into the scientific underpinnings of calories, their role in metabolism, and their influence on energy balance. Let's begin by examining the fundamental differences between cal and calories and why they are important in your daily life.
- 70 Cast
- List Of Ontario Millstores
- Amazon Prime Call Center
- Charlieheen Ashton Kutcher
- Alice Braga Moraes
Table of Contents
- What Are Calories?
- Difference Between Cal and Calories
- Calories in Food
- Calories and Metabolism
- Measuring Energy
- Calories and Weight Management
- Calories and Exercise
- Caloric Deficit
- Caloric Surplus
- Conclusion
Exploring the Concept of Calories
Calories are units of energy that measure the heat required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of water by one degree Celsius. In the realm of nutrition, calories quantify the energy derived from food and beverages. Gaining insight into what calories represent is the cornerstone of making healthier dietary decisions.
Calories are indispensable for sustaining vital bodily functions, such as respiration, digestion, and physical movement. The body requires a specific caloric intake each day to support these processes, with the exact amount depending on factors like age, gender, weight, and activity level. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), the average adult needs approximately 2,000–2,500 calories daily. However, individual needs can vary widely based on personal circumstances and lifestyle.
Understanding your unique caloric requirements is essential for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. By aligning your calorie consumption with your body's needs, you can optimize your health and well-being.
- Msnbc Lawrence O Donnell Last Word
- Deandre Hopkins Height Weight
- Country Hills Ford
- Norman Names
- South Bend A Breaking News
Clarifying the Difference Between Cal and Calories
What Does "Cal" Mean?
The term "cal" refers to the small calorie, which measures the energy needed to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius. This unit is predominantly utilized in scientific research and laboratory settings. In everyday discussions about nutrition, however, the term "cal" is seldom encountered.
What Are Calories?
When most people refer to calories, they are actually talking about kilocalories (kcal). A kilocalorie equals 1,000 small calories and is the standard unit for measuring the energy content of food. For simplicity, kilocalories are often referred to as "calories" in nutritional contexts.
The primary distinction between cal and calories lies in their scale. While cal measures small amounts of energy, calories (kcal) quantify larger quantities that are more relevant to human nutrition. Recognizing this difference is vital for interpreting nutritional labels and making informed dietary decisions.
The Role of Calories in Food
Food supplies the energy our bodies require to function. Different types of food contain varying calorie amounts, which depend on their macronutrient composition. The three primary macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—are the main sources of calories in our diet.
- Carbohydrates: Provide 4 calories per gram and serve as the body's primary energy source.
- Proteins: Also supply 4 calories per gram and are essential for building and repairing tissues.
- Fats: Deliver 9 calories per gram and are the most calorie-dense macronutrient.
It's crucial to recognize that not all calories are equal. The quality of the food you consume significantly impacts your overall health. Whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, provide essential nutrients and fiber. On the other hand, processed foods often contain empty calories with minimal nutritional value, making them less beneficial for your health.
Calories and Their Role in Metabolism
Metabolism encompasses the chemical processes that sustain life within the body. These processes require energy, which is derived from the calories we consume. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) represents the number of calories your body needs to perform basic functions while at rest.
Various factors influence metabolism, including:
- Age: Metabolism tends to slow down as we grow older.
- Gender: Men generally have higher metabolic rates than women due to differences in muscle mass.
- Body Composition: Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue, meaning individuals with higher muscle mass typically have faster metabolisms.
- Activity Level: Physical activity increases calorie expenditure and can enhance metabolism over time.
Comprehending your metabolism is key to managing caloric intake and achieving your health objectives. By aligning your calorie consumption with your metabolic needs, you can optimize your energy balance.
How Energy Is Measured
Calorimetry: The Science of Energy Measurement
Calorimetry is the scientific method used to measure heat transfer and is employed to determine the calorie content of food. Bomb calorimeters are commonly used in laboratories to assess the energy released when food is combusted. This technique provides an accurate estimation of the calories in a particular food item.
Nutritional Labels: A Key Resource for Calorie Awareness
Beyond laboratory measurements, nutritional labels offer valuable information about the calorie content of packaged foods. These labels detail the number of calories per serving and break down the macronutrient composition. Learning to read and interpret nutritional labels is an essential skill for anyone aiming to manage their caloric intake effectively.
The Connection Between Calories and Weight Management
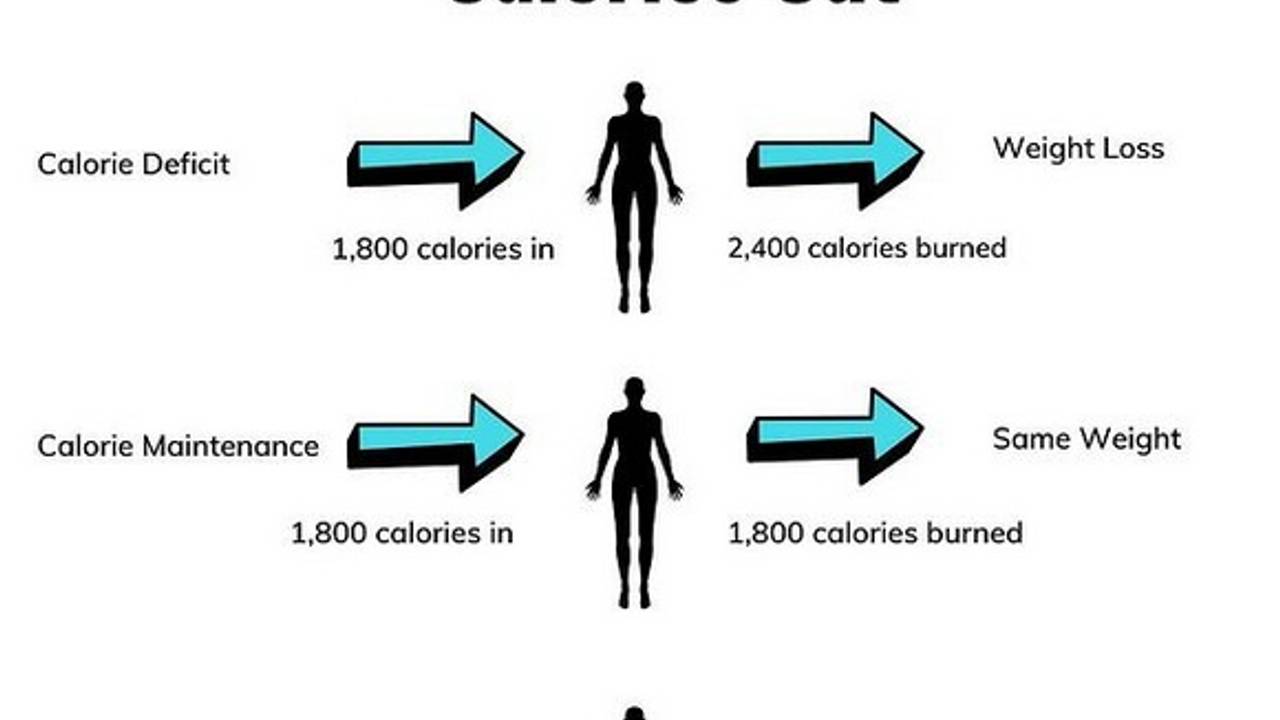
Weight management is intrinsically linked to caloric balance. To maintain a healthy weight, the calories consumed should equal the calories expended. When calorie intake surpasses expenditure, the excess energy is stored as body fat, leading to weight gain. Conversely, when calorie expenditure exceeds intake, the body taps into stored fat for energy, resulting in weight loss.
Achieving caloric balance necessitates careful attention to both diet and physical activity. By monitoring your caloric intake and modifying your food choices accordingly, you can achieve and sustain a healthy weight.
The Impact of Exercise on Calorie Expenditure
Exercise is a powerful tool for increasing calorie expenditure and enhancing overall health. Different types of physical activity burn varying amounts of calories, depending on intensity, duration, and individual factors such as weight and fitness level.
For instance:
- Walking: Burns approximately 100–200 calories per hour, contingent on speed and terrain.
- Running: Burns around 500–800 calories per hour, depending on pace and distance.
- Strength Training: Burns 200–400 calories per hour and promotes muscle growth, which can elevate metabolism over time.
Integrating regular exercise into your routine is an excellent way to manage calories and improve overall fitness. By combining physical activity with a balanced diet, you can optimize your health and well-being.
The Importance of Caloric Deficit for Weight Loss
A caloric deficit occurs when the calories consumed are fewer than the calories expended. This state is essential for weight loss, as it prompts the body to utilize stored fat for energy. Creating a sustainable caloric deficit involves reducing calorie intake and increasing physical activity.
However, it's crucial to avoid extreme calorie restriction, as it can lead to nutrient deficiencies and other health issues. A moderate caloric deficit of 500–1,000 calories per day is typically recommended for safe and effective weight loss. By adopting a balanced approach, you can achieve your weight loss goals without compromising your health.
Caloric Surplus: Building Muscle and Restoring Health
A caloric surplus arises when the calories consumed exceed the calories expended. This state is necessary for weight gain, especially for individuals aiming to build muscle or recover from illness. Creating a caloric surplus requires careful planning to ensure adequate nutrient intake while minimizing excessive fat gain.
For muscle development, a caloric surplus of 250–500 calories per day is generally recommended. This additional energy should come from nutrient-rich foods, such as lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. By focusing on quality nutrition, you can support muscle growth and optimize your health.
Final Thoughts on Calories and Your Health
In summary, understanding the distinction between cal and calories is fundamental for making informed dietary choices and managing your health effectively. By appreciating the role of calories in metabolism, weight management, and exercise, you can take control of your energy balance and achieve your fitness aspirations.
We encourage you to apply the insights gained from this article to your daily life. Begin by tracking your caloric intake, adjusting your food choices, and incorporating regular exercise into your routine. Don't hesitate to share this article with others who may benefit from it, and feel free to leave a comment below with your thoughts or questions.
Sources:
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA)
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Harvard Health Publishing


Detail Author:
- Name : Arielle Ward
- Username : flatley.fay
- Email : patricia40@weimann.com
- Birthdate : 2001-08-26
- Address : 97148 Paxton Passage Suite 691 Goyettemouth, OH 68207
- Phone : 603.457.2323
- Company : Kuhn and Sons
- Job : Aircraft Launch Specialist
- Bio : Facilis consectetur corrupti odit corrupti nobis. Minima omnis provident deserunt provident sint eum quidem incidunt. Eligendi aut deleniti debitis iure. Veniam velit delectus ut vitae ut.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/skunze
- username : skunze
- bio : Aut rerum voluptatem distinctio eligendi qui.
- followers : 2679
- following : 1068
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/kunze1986
- username : kunze1986
- bio : Sed quidem unde sunt dolore. Mollitia ad repellat hic. Excepturi temporibus voluptatum et placeat.
- followers : 2868
- following : 832
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/sofia_kunze
- username : sofia_kunze
- bio : Ab eaque quidem iure. Velit molestias sint ab voluptatem sed.
- followers : 823
- following : 1443
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/skunze
- username : skunze
- bio : Qui quasi asperiores laborum iusto beatae occaecati. Minus nemo ipsum id rerum. Corrupti cupiditate cum et doloremque.
- followers : 1768
- following : 2230