Delving into the concept of color opposites can significantly enhance your creativity and deepen your understanding of color theory. If you've ever wondered what color is opposite of blue, this article will provide an in-depth exploration. Whether you're an artist, designer, or simply curious about colors, this guide is tailored for you.
Color theory plays a pivotal role across various disciplines, from art to branding. Understanding the opposite of blue and how colors interact can profoundly influence your work or personal projects. This article will take you on a journey to explore the concept of color opposites, focusing on the intricate nuances of blue's complementary color.
By the time you finish reading, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of the color opposite to blue and how it can be applied in diverse contexts. Let's begin this colorful exploration!
- Koa Campground Near Dollywood
- Teddywims Genre
- When Did Bob Marley Die Age
- Rochester Civic Center
- Theaters Inalinas Ca
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Fundamentals of Color Theory
- What Color Is the True Opposite of Blue?
- The Color Wheel: A Key to Unlocking Color Relationships
- Complementary Colors: The Art of Contrast
- The Deep Meaning and Symbolism Behind Blue
- The Vibrant Symbolism and Meaning of Orange
- Applications of Opposite Colors in Design and Art
- The Psychology of Color in Marketing Strategies
- The Role of Complementary Colors in Fashion
- Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Color Theory
Understanding the Fundamentals of Color Theory
Color theory forms the bedrock of understanding how colors interact and influence each other. This expansive field encompasses a variety of concepts, including the color wheel, color harmony, and the various contexts in which colors are employed. Artists, designers, and marketers alike rely heavily on color theory to craft visually captivating and impactful designs.
At its essence, color theory revolves around the principles of primary, secondary, and tertiary colors. These colors collectively create the foundation of the color wheel, a tool essential for identifying complementary colors and developing cohesive color schemes. For instance, primary colors such as red, blue, and yellow cannot be created by mixing other colors. Secondary colors, like orange, green, and purple, emerge from blending two primary colors. Tertiary colors arise from the fusion of primary and secondary colors, resulting in unique hues like red-orange or blue-green.
What Color Is the True Opposite of Blue?
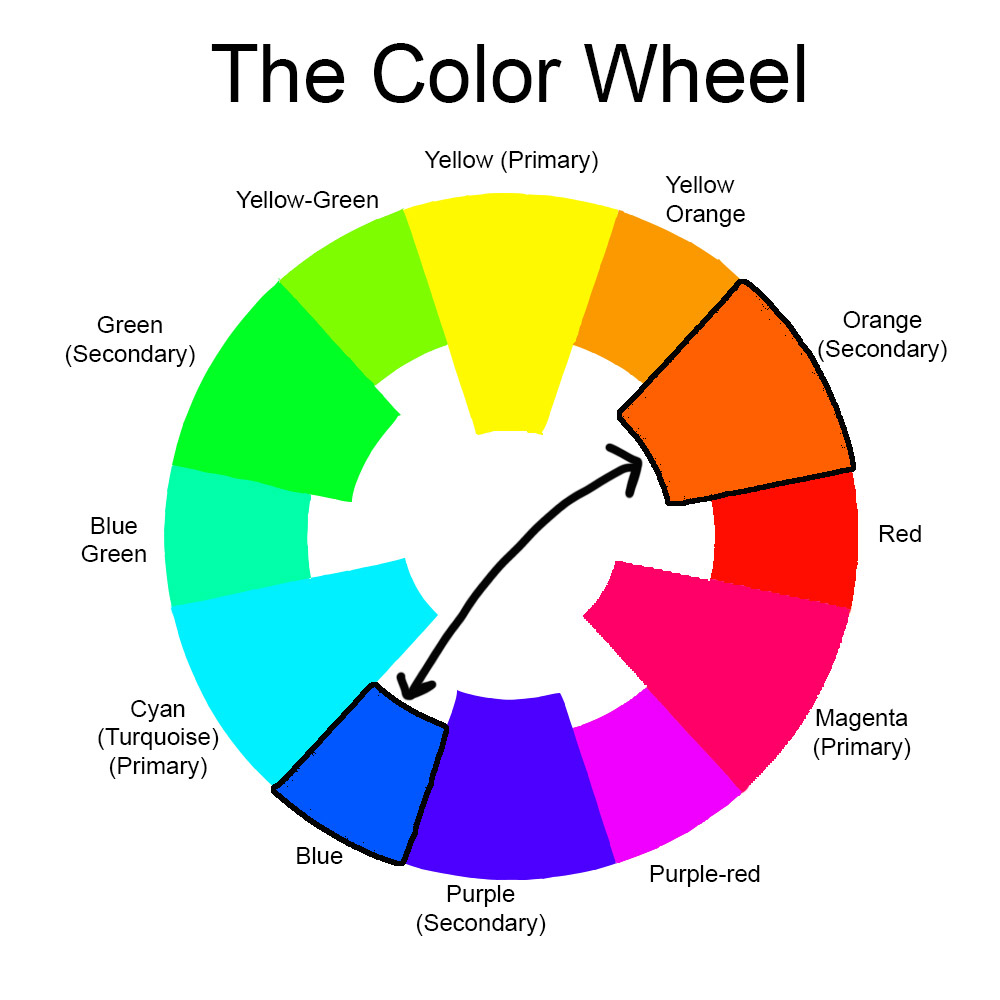
The true opposite of blue is orange. This relationship is rooted in the structure of the color wheel, where complementary colors are positioned directly across from one another. When blue and orange are placed adjacent to each other, they produce a striking contrast that elevates the visual appeal of both colors, creating a harmonious balance.
- Donald Trump Children Names
- North Hills Aaa
- Country Hills Ford
- Charlieheen Ashton Kutcher
- How Old Jack Black
Complementary colors, such as blue and orange, collaborate to produce balanced and aesthetically pleasing designs. This principle is widely applied in art, interior design, and digital media to capture attention and evoke specific emotions. The interplay between these colors ensures that designs are not only visually stimulating but also emotionally resonant.
The Color Wheel: A Key to Unlocking Color Relationships
History and Evolution of the Color Wheel
The color wheel was first conceptualized by Sir Isaac Newton in 1666. This circular diagram illustrates the spectrum of colors and their interrelationships. Over time, the color wheel has evolved to encompass various forms, including the traditional artist's color wheel and the modern digital color wheel.
The artist's color wheel is based on the subtractive color model, which involves the mixing of pigments. Conversely, the digital color wheel operates on the additive color model, where colors are generated through the combination of light. Both models offer unique insights into the world of color and its applications.
How the Color Wheel Functions
The color wheel is segmented into three primary categories: primary, secondary, and tertiary colors. Primary colors consist of red, blue, and yellow, while secondary colors include orange, green, and purple. Tertiary colors arise from blending a primary color with a secondary color, yielding hues such as red-orange or blue-green.
On the color wheel, complementary colors are positioned directly opposite each other. For instance, blue is opposite orange, red is opposite green, and yellow is opposite purple. This arrangement facilitates the identification of color pairs that create dynamic contrasts and harmonious designs.
Complementary Colors: The Art of Contrast
Complementary colors are pairs of colors that exhibit a sharp contrast when placed side by side. This contrast generates a visually engaging effect that draws attention and enhances the overall design. In addition to blue and orange, other notable complementary color pairs include:
- Red and Green
- Yellow and Purple
- Cyan and Red-Orange
These color combinations are extensively utilized across various fields, including graphic design, web development, and interior design. By mastering the use of complementary colors, designers can create compositions that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly functional.
The Deep Meaning and Symbolism Behind Blue
Blue is a universally popular color that symbolizes trust, loyalty, and wisdom. It is frequently associated with the sky and the sea, evoking feelings of tranquility and serenity. In many cultures, blue is regarded as a masculine color and is commonly used in corporate branding to convey professionalism and reliability.
However, the meaning of blue can differ based on the context and cultural background. For instance, in Western cultures, blue is often linked to sadness or depression, as reflected in phrases like "feeling blue." In contrast, in Eastern cultures, blue represents immortality and eternity, showcasing its diverse symbolic interpretations.
The Vibrant Symbolism and Meaning of Orange
Orange is a lively and energetic color that embodies enthusiasm, creativity, and adventure. It is often associated with the autumn season, harvest, and warmth. In numerous cultures, orange is viewed as a color of spirituality and transformation, as evidenced by the traditional robes of Buddhist monks.
Similar to blue, the meaning of orange can vary depending on the context and culture. In Western cultures, orange is closely tied to Halloween and fall festivities. In India, orange (or saffron) holds sacred significance, symbolizing purity and holiness, further highlighting its cultural importance.
Applications of Opposite Colors in Design and Art
Utilizing Complementary Colors in Artistic Compositions
In the realm of art, complementary colors are employed to create contrast and balance within a composition. By positioning blue and orange next to each other, artists can highlight specific elements and evoke powerful emotions. This technique is especially effective in paintings, illustrations, and digital art.
For example, Vincent van Gogh masterfully utilized complementary colors in his iconic works, such as "The Starry Night," where the interplay between blue and orange skies generates a dynamic and expressive atmosphere. This approach underscores the significance of complementary colors in enhancing artistic expression.
Implementing Complementary Colors in Web Design
In web design, complementary colors are leveraged to create visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces. By integrating blue and orange into a website's color scheme, designers can emphasize critical elements, such as buttons, links, and calls to action. This contrast not only improves usability but also enhances the overall user experience.
The Psychology of Color in Marketing Strategies
The psychology of color plays a critical role in marketing and branding. Colors have the power to influence consumer behavior and decision-making, making them an indispensable tool for businesses. For example, blue is frequently used in corporate branding to convey trust and reliability, while orange is employed to instill a sense of urgency and excitement.
Research has demonstrated that color can impact mood, perception, and even purchasing decisions. By comprehending the psychology of color, businesses can craft marketing campaigns that resonate with their target audience and yield tangible results.
The Role of Complementary Colors in Fashion
In the fashion industry, complementary colors are utilized to create bold and striking looks. Designers often incorporate blue and orange into their collections to add depth and contrast to their designs. This combination is particularly prevalent in sportswear and activewear, where vibrant colors are crucial for visibility and performance.
Moreover, complementary colors can enhance personal style and contribute to a balanced wardrobe. By experimenting with blue and orange in various shades and intensities, individuals can explore their fashion choices and express their unique personalities.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Color Theory
In summary, the color opposite of blue is orange. This complementary color pair is fundamental in color theory and offers countless applications in art, design, marketing, and fashion. By grasping the principles of complementary colors, you can create visually stunning and impactful designs that engage and inspire your audience.
We invite you to delve deeper into the captivating world of color theory and experiment with diverse color combinations. Feel free to leave a comment below to share your thoughts or pose any questions. Be sure to explore our other articles for additional insights into the mesmerizing realm of colors!
Data sources:

Detail Author:
- Name : Mabel Rath
- Username : fwitting
- Email : emmanuel90@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1989-03-31
- Address : 8508 Dan Mountain Andrewburgh, ME 85973
- Phone : 540-867-3213
- Company : Balistreri and Sons
- Job : Biological Technician
- Bio : Error ab eos soluta aut nesciunt sint sequi provident. Commodi quos architecto autem occaecati omnis eveniet. Ea id facilis corporis aut minima enim id. Quis odit voluptatibus quae voluptas id.
Socials
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@keara6295
- username : keara6295
- bio : Consequatur in a aperiam rerum iusto. Et maiores debitis expedita eum quo.
- followers : 5856
- following : 51
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/haley1971
- username : haley1971
- bio : Aspernatur praesentium ipsa porro totam vel et perferendis velit. Facilis ex possimus sunt sit dolore.
- followers : 4945
- following : 413
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/keara9601
- username : keara9601
- bio : Recusandae tenetur tempora sit aut quia eos. Laborum dicta quis ipsa eos repudiandae aut sit.
- followers : 1615
- following : 1297
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/haley2011
- username : haley2011
- bio : Consequuntur rerum earum quibusdam velit.
- followers : 6792
- following : 1248
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/keara3823
- username : keara3823
- bio : Amet esse amet accusantium rem nulla molestiae.
- followers : 2651
- following : 1570