Blue, one of the most universally cherished colors, embodies serenity, trust, and stability. Yet, have you ever wondered about its counterpart on the color spectrum? Understanding the concept of color opposites is fundamental to mastering color theory, which plays a pivotal role in design, art, and even psychology. Whether you're an aspiring artist, a seasoned designer, or simply curious about colors, this article will take a deep dive into the intriguing concept of the opposite color of blue.
The idea of blue's opposite color has intrigued professionals and enthusiasts alike. From its scientific underpinnings to its practical implications, this topic opens doors to endless creative possibilities. By delving into the intricacies of color theory, we can gain a deeper understanding of how colors interact and complement one another.
In this article, we will guide you through the captivating world of color opposites. We'll explore everything from the scientific principles behind color opposites to their real-world applications. By the end, you will possess a comprehensive understanding of the opposite color of blue and how it can be effectively utilized across various disciplines.
- Joe Biden Political Career
- Actress Emily Hampshire
- Temperature For Medium Rareteak
- Power Outage Entergy
- Best Blue Oyster Cultongs
Contents Overview
- Understanding Color Theory
- Defining Opposite Colors
- The Role of Blue in the Color Wheel
- A Scientific View on Opposite Colors
- Practical Uses of Opposite Colors
- The Psychology Behind Opposite Colors
- Opposite Colors in Design and Art
- Applications in the Fashion Industry
- Technology and Digital Media Insights
- Final Thoughts
Understanding Color Theory
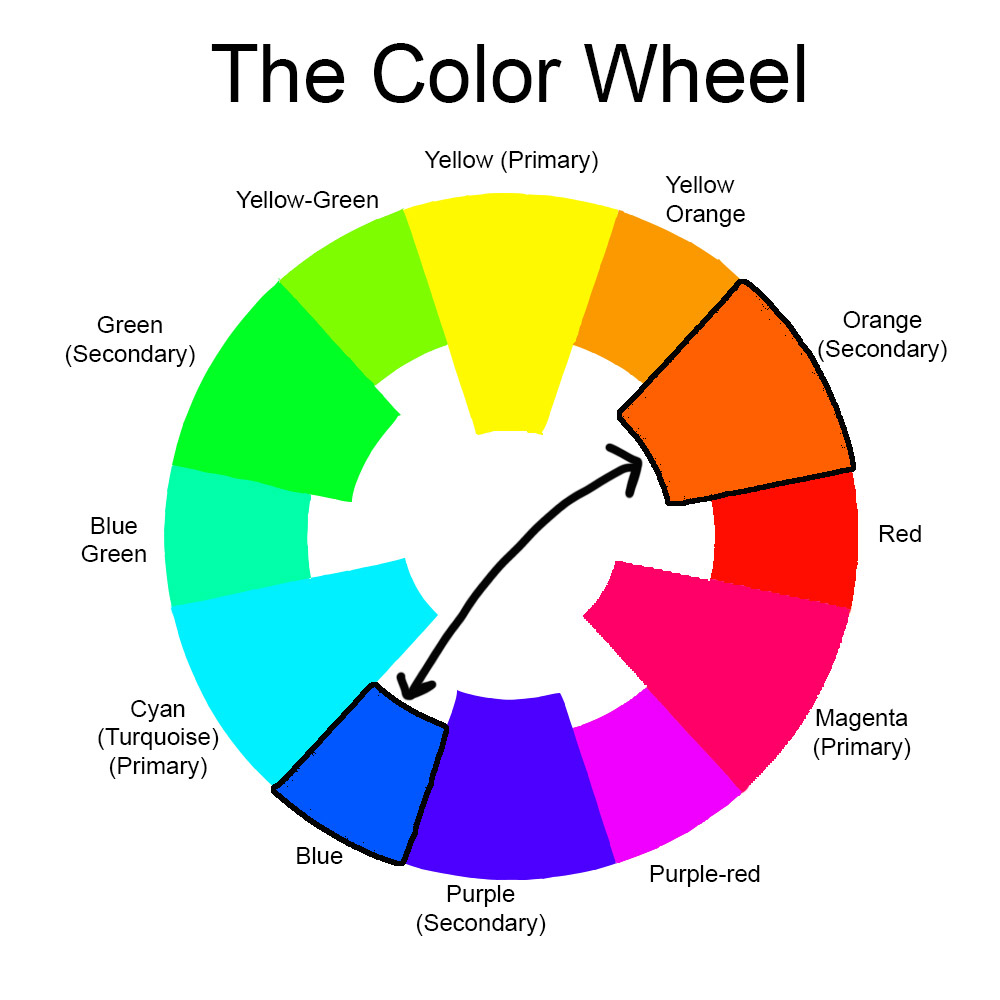
Color theory forms the backbone of how colors interact and influence each other. It is a collection of principles used to craft harmonious and visually captivating color combinations. Artists, designers, and even marketers depend on color theory to evoke specific emotions and create aesthetic appeal. The color wheel, an essential tool in color theory, aids in identifying complementary, analogous, and opposite colors.
Opposite colors, also known as complementary colors, are those situated directly across from each other on the color wheel. These colors produce a dramatic contrast when juxtaposed, resulting in visually engaging and dynamic effects. Grasping the concept of blue's opposite color involves exploring the foundational principles of color theory.
Why Does Color Theory Matter?
Color theory is crucial because it provides a structured approach to creating visually appealing designs. By comprehending how colors interact, you can craft balanced and harmonious compositions. Whether you're designing a logo, painting a masterpiece, or decorating your home, color theory serves as a guiding framework for making informed decisions.
- Enhances visual communication
- Intensifies emotional impact
- Produces professional and polished designs
Defining Opposite Colors
Opposite colors, or complementary colors, are positioned directly across from each other on the color wheel. When paired, these colors generate a striking contrast that captivates the eye. For instance, the opposite color of blue is orange, a relationship rooted in the principles of color theory and how our eyes perceive colors.
How Are Opposite Colors Identified?
Opposite colors are identified by their placement on the color wheel. This circular diagram represents the spectrum of colors and is divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary hues. Primary colors include red, blue, and yellow, while secondary colors consist of green, orange, and purple. Tertiary colors arise from blending primary and secondary colors.
Orange stands as the opposite color of blue because it is positioned directly across from it on the color wheel. This relationship fosters a harmonious balance that is visually pleasing.
The Role of Blue in the Color Wheel
Blue, a primary color, holds a prominent position on the color wheel. It is often linked with tranquility, reliability, and steadfastness. As a primary color, blue cannot be created by blending other colors, yet it serves as a foundation for generating a vast array of shades and hues.
Unpacking Blue's Complementary Relationship
Blue's complementary color is orange. This connection stems from the principles of color theory, where colors positioned directly across from each other on the color wheel create a striking contrast. The pairing of blue and orange is frequently employed in design and art to craft dynamic and visually appealing compositions.
Research published in the Journal of Color Science highlights how complementary colors amplify visual perception and evoke profound emotional responses. This makes them an invaluable resource in various domains, such as marketing, design, and art.
A Scientific View on Opposite Colors
From a scientific perspective, opposite colors are grounded in how our eyes perceive light. The human eye contains photoreceptor cells called cones, which detect color. There are three types of cones, each sensitive to different wavelengths of light: red, green, and blue.
When we observe a color, our cones detect the wavelengths of light reflected by that color. Opposite colors like blue and orange create a powerful contrast because they stimulate distinct sets of cones. This contrast enhances visual perception, making the colors appear more vibrant and vivid.
How Do Opposite Colors Influence Perception?
Opposite colors influence perception by generating a high-contrast effect. This effect arises from how our brains process visual information. Upon seeing complementary colors, our brains naturally enhance the contrast between them, making them appear more dynamic and engaging.
Studies featured in the Color Research and Application Journal reveal that complementary colors improve visual clarity and focus. This makes them particularly valuable in fields like graphic design, where clarity and impact are paramount.
Practical Uses of Opposite Colors
The concept of opposite colors boasts numerous practical applications across various industries. From design and art to marketing and technology, understanding color interactions can elevate the effectiveness of visual communication.
Design and Art
In design and art, opposite colors are frequently utilized to craft visually striking compositions. For instance, the pairing of blue and orange is commonly found in logos, advertisements, and packaging. This combination achieves a sense of balance and harmony while maintaining a strong visual impact.
Marketing
In marketing, opposite colors are employed to capture attention and evoke emotions. The contrast between complementary colors makes them ideal for creating eye-catching advertisements and promotional materials. Brands often leverage complementary colors to distinguish themselves from competitors and establish a memorable brand identity.
Technology
In the technology sector, opposite colors enhance user experience. User interface (UI) designers frequently incorporate complementary colors to design visually appealing and functional interfaces. This improves usability and makes digital platforms more engaging.
The Psychology Behind Opposite Colors
The psychology of color significantly influences how we perceive and respond to colors. Opposite colors, such as blue and orange, can elicit strong emotional reactions and shape our behavior. Understanding the psychological effects of color empowers designers and marketers to create more impactful visual communication.
Emotional Effects of Blue and Orange
Blue is commonly associated with calmness, stability, and trust, while orange is linked to energy, enthusiasm, and creativity. The fusion of these two colors creates a balance between tranquility and excitement, making it versatile for various applications.
Research published in the Journal of Consumer Psychology indicates that complementary colors heighten emotional engagement and improve brand recall. This makes them especially effective in marketing and advertising strategies.
Opposite Colors in Design and Art
In the realm of design and art, opposite colors serve as a potent tool for crafting dynamic and visually captivating compositions. Artists and designers utilize complementary colors to achieve balance, harmony, and contrast in their work. The pairing of blue and orange, for instance, is often seen in paintings, graphic design, and interior design.
Tips for Incorporating Opposite Colors in Design
- Use complementary colors sparingly to create focal points
- Balance the intensity of opposite colors to preserve harmony
- Experiment with various shades and hues to produce unique effects
By comprehending how opposite colors interact, designers and artists can create compositions that are not only visually striking but also emotionally engaging.
Applications in the Fashion Industry
The fashion industry frequently embraces opposite colors to design bold and stylish creations. The combination of blue and orange, for example, is often seen in clothing, accessories, and home decor. This pairing achieves a sense of balance and harmony while retaining a strong visual impact.
Emerging Trends in Fashion
Recent fashion trends highlight the use of complementary colors to create statement pieces. Designers are incorporating blue and orange in innovative ways, such as pairing them with neutral tones or using them as accent colors. This trend reflects a growing appreciation for bold and daring design choices.
According to industry experts, the use of complementary colors in fashion is anticipated to grow in popularity. This trend is fueled by consumer demand for distinctive and visually appealing designs.
Technology and Digital Media Insights
In the field of technology and digital media, opposite colors play a vital role in enhancing user experience. UI designers and web developers utilize complementary colors to design visually appealing and functional interfaces. The combination of blue and orange, for example, is often employed in digital interfaces to achieve a sense of balance and harmony.
Best Practices for Using Opposite Colors in Digital Media
- Use complementary colors to establish visual hierarchy
- Balance the intensity of opposite colors to ensure readability
- Test color combinations across different devices for consistency
By adhering to these best practices, designers and developers can craft digital interfaces that are both visually appealing and user-friendly.
Final Thoughts
In summary, understanding the opposite color of blue is essential for anyone involved in design, art, marketing, or technology. The pairing of blue and orange creates a striking contrast that is both visually appealing and emotionally engaging. By applying the principles of color theory, you can craft compositions that are balanced and dynamic.
We encourage you to experiment with opposite colors in your projects. Whether you're designing a logo, creating a painting, or developing a digital interface, the use of complementary colors can elevate the effectiveness of your work. Feel free to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and explore more articles on our website for deeper insights into the captivating world of color theory.

Detail Author:
- Name : Jillian Roob Sr.
- Username : wferry
- Email : emery61@yahoo.com
- Birthdate : 1990-11-29
- Address : 77566 Joel Fords Lake Maudland, GA 52300-1787
- Phone : 1-629-708-4705
- Company : Kub, DuBuque and Stark
- Job : Retail Salesperson
- Bio : Animi voluptatem odio praesentium odio esse est. Ullam dolore aut in facere sit laborum molestiae. Iure vero aliquid sed est aut praesentium nobis.
Socials
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@orval.kemmer
- username : orval.kemmer
- bio : Aliquid quaerat consectetur odit perspiciatis. Dolorem deleniti ullam qui.
- followers : 3454
- following : 694
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/kemmer2008
- username : kemmer2008
- bio : Nulla placeat aspernatur fuga amet.
- followers : 5150
- following : 2018
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/kemmer1974
- username : kemmer1974
- bio : Eum error autem quia. Voluptatem ut deleniti corporis eum. Aut est explicabo quia error debitis quia.
- followers : 5241
- following : 2701
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/orvalkemmer
- username : orvalkemmer
- bio : Aut ut quia accusamus quae.
- followers : 3407
- following : 440