Selecting the appropriate disk partitioning system is fundamental to achieving optimal performance and safeguarding data integrity on your computer. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a professional IT administrator, or a newcomer to computing, distinguishing between MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) is crucial. Both systems possess distinct strengths and limitations, making it vital to assess your specific requirements before making a decision.
In this detailed article, we will delve into the intricacies of MBR and GPT, dissecting their features, advantages, and disadvantages. By the conclusion, you'll have a clear understanding of which system aligns best with your needs—whether you're managing a personal computer or overseeing enterprise-level data storage solutions.
As technology progresses, the demand for efficient and reliable disk partitioning systems has increased significantly. MBR and GPT stand out as two of the most popular options available today, each offering unique capabilities tailored to various use cases. Let's explore the details to assist you in making an informed choice.
Table of Contents
- Overview of MBR
- Understanding GPT
- Comparing MBR and GPT Features
- Key Differences Between MBR and GPT
- Addressing Compatibility Challenges
- Performance Analysis
- Scenarios for Using MBR
- When GPT is the Better Choice
- Steps to Convert MBR to GPT
- How to Convert GPT to MBR
- Final Thoughts
Overview of MBR
The Master Boot Record (MBR) is one of the earliest disk partitioning systems in computing, introduced in 1983. Over the decades, it has remained a reliable standard. MBR enables users to divide their hard drives into partitions, facilitating better data and operating system management.
A significant characteristic of MBR is its limitation to four primary partitions per disk. If additional partitions are required, one of these primary partitions can be converted into an extended partition, which can accommodate multiple logical partitions. While this setup works well for basic needs, it may pose challenges for users with more complex storage requirements.
Advantages of MBR
- Extensive compatibility with older systems
- Straightforward setup and management
- Suitable for smaller disks and straightforward partitioning needs
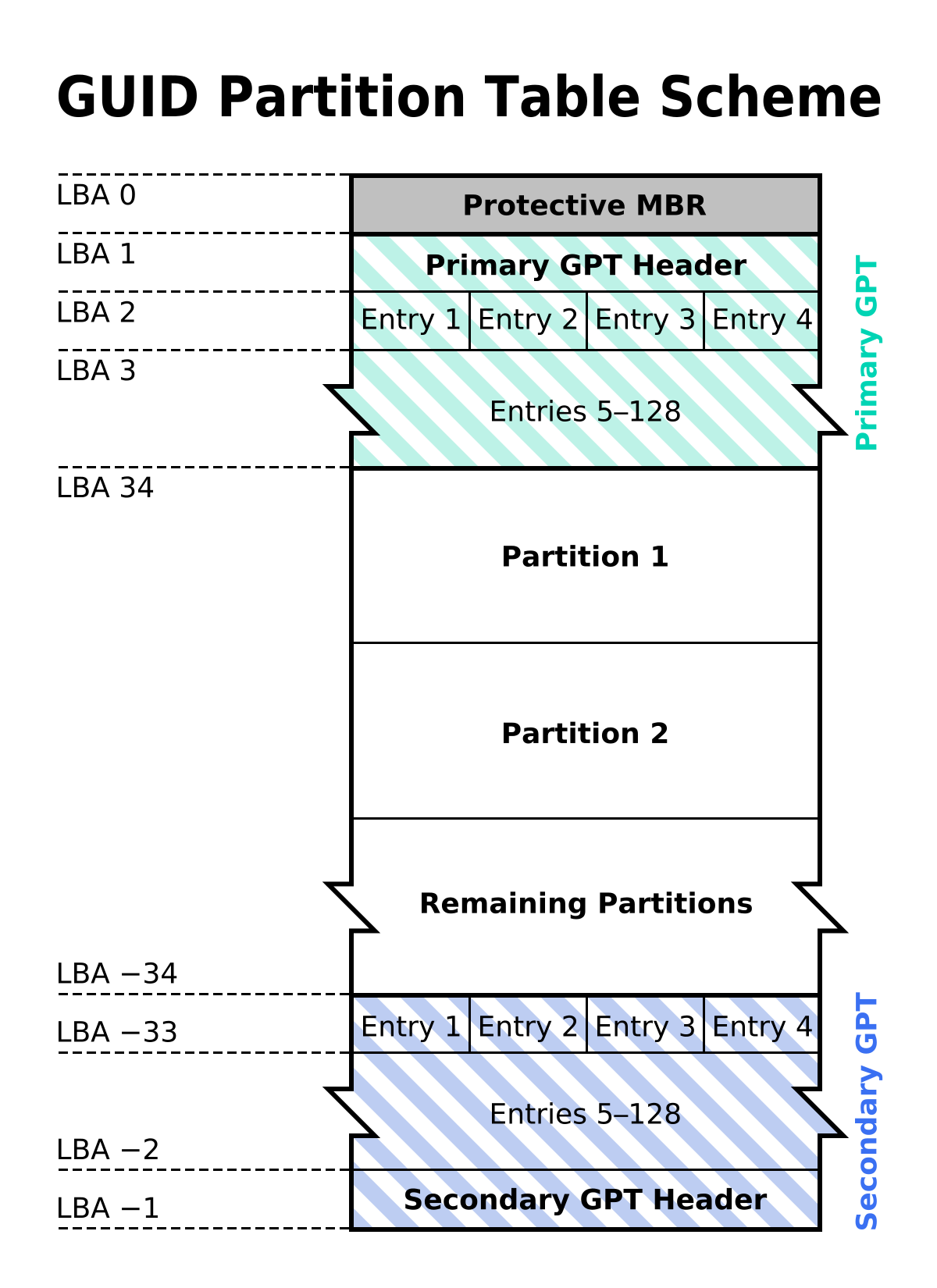
Understanding GPT
The GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a modern disk partitioning system introduced as part of the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) standard. GPT surpasses MBR in several ways, including support for larger disks and more partitions, making it ideal for advanced storage configurations.
GPT employs a globally unique identifier (GUID) for each partition, ensuring that partitions are uniquely identifiable across multiple disks. This feature enhances data integrity and minimizes the risk of partition conflicts, offering a more robust solution for modern computing environments.
Advantages of GPT
- Supports disks exceeding 2TB in size
- Allows up to 128 partitions per disk
- Provides enhanced data protection and reliability
Comparing MBR and GPT Features
When evaluating MBR and GPT, it's essential to consider their defining features to determine which system best suits your needs. Below is a detailed comparison of their primary attributes:
- MBR supports disks up to 2TB, while GPT accommodates disks larger than 2TB.
- MBR permits a maximum of four primary partitions, whereas GPT supports up to 128 partitions.
- GPT ensures superior data integrity through GUIDs and checksums, whereas MBR relies on simpler partition tables.
Key Differences Between MBR and GPT
The distinctions between MBR and GPT extend beyond their fundamental features. These systems differ significantly in terms of compatibility, performance, and ease of use. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision.
Compatibility
MBR enjoys widespread support on older systems and legacy BIOS firmware, making it a dependable choice for users with outdated hardware. Conversely, GPT requires UEFI firmware for optimal functionality, which may limit its compatibility with certain older systems.
Performance
GPT typically delivers superior performance, particularly for large disks and complex partitioning setups. Its ability to handle extensive storage and numerous partitions efficiently makes it a preferred choice for modern computing environments.
Addressing Compatibility Challenges
One of the primary concerns when choosing between MBR and GPT is compatibility. While MBR is compatible with virtually all systems, GPT may face limitations on older hardware. It's essential to verify your system's firmware and operating system support before transitioning to GPT.
For instance, Windows operating systems prior to Windows 8 may not fully support GPT, especially if they rely on legacy BIOS rather than UEFI. Similarly, some Linux distributions may necessitate additional configuration to work seamlessly with GPT partitions.
Performance Analysis
In terms of performance, GPT often surpasses MBR, especially on larger disks. Its capacity to create more partitions and manage extensive storage spaces efficiently makes it an excellent choice for high-performance computing environments. However, for smaller disks and simpler setups, MBR can still provide adequate performance with minimal overhead.
Scenarios for Using MBR
MBR is ideal for users who:
- Operate older hardware reliant on legacy BIOS
- Require compatibility with a broad range of systems
- Do not need to work with disks larger than 2TB
For these users, the simplicity and reliability of MBR make it a practical and cost-effective solution.
When GPT is the Better Choice
GPT is recommended for users who:
- Utilize modern hardware that supports UEFI
- Need to manage large disks or complex partitioning setups
- Prioritize data integrity and reliability
With its advanced features and capabilities, GPT is well-suited for demanding computing environments, ensuring enhanced performance and security.
Steps to Convert MBR to GPT
Converting an MBR disk to GPT can be a straightforward process if executed correctly. However, it's crucial to back up your data before altering your disk partitioning system. Below are the steps to convert an MBR disk to GPT:
- Backup all critical data from the disk.
- Open Disk Management in Windows or use a third-party partitioning tool.
- Select the disk you wish to convert and choose the "Convert to GPT" option.
- Follow the prompts to complete the conversion process.
Considerations
Some systems may require a clean install of the operating system after converting to GPT, particularly if they rely on legacy BIOS. Always confirm compatibility before proceeding with the conversion.
How to Convert GPT to MBR
Converting a GPT disk to MBR is feasible, though it may involve additional steps depending on your system configuration. Below is a guide to assist you through the process:
- Backup all data from the GPT disk.
- Open Disk Management or use a partitioning tool.
- Select the disk and choose the "Convert to MBR" option.
- Follow the prompts to complete the conversion.
Important Notes
Converting from GPT to MBR may result in the loss of some partitions, especially if the disk contains more than four primary partitions. Always ensure that your data is securely backed up before making any changes to your disk partitioning system.
Final Thoughts
In summary, both MBR and GPT provide valuable solutions for disk partitioning, each with its own unique strengths and limitations. MBR remains a dependable option for users with older hardware and simpler storage requirements, while GPT offers advanced capabilities for modern computing environments.
To maximize the efficiency of your disk partitioning system, carefully consider your specific needs and the compatibility of your hardware and software. Whether you choose MBR or GPT, understanding their features and differences will help you optimize your storage setup for peak performance and reliability.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with MBR and GPT in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore our other articles for further insights into computing and technology. Thank you for reading!


Detail Author:
- Name : Emilia Graham MD
- Username : jamaal61
- Email : carey.boehm@pagac.org
- Birthdate : 2003-05-18
- Address : 32069 Hegmann Fort Suite 203 West Shanel, SD 40834-6772
- Phone : 475-949-2364
- Company : Hermann-Becker
- Job : Watch Repairer
- Bio : Voluptatem repellendus similique vero distinctio esse nemo nihil. Quo dolor provident impedit non aliquid et. Et nulla iusto non neque saepe voluptatem.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/esther_cummerata
- username : esther_cummerata
- bio : Error adipisci ut cumque natus consequatur. Id omnis et sint. Earum nisi id repellat dolores.
- followers : 3897
- following : 190
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@esther.cummerata
- username : esther.cummerata
- bio : Doloribus amet doloremque sapiente voluptatem ipsa dolores exercitationem.
- followers : 6333
- following : 1037
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/ecummerata
- username : ecummerata
- bio : Quia molestias aut labore laborum qui qui cumque ipsa.
- followers : 4391
- following : 1000